How many electrons in f orbital
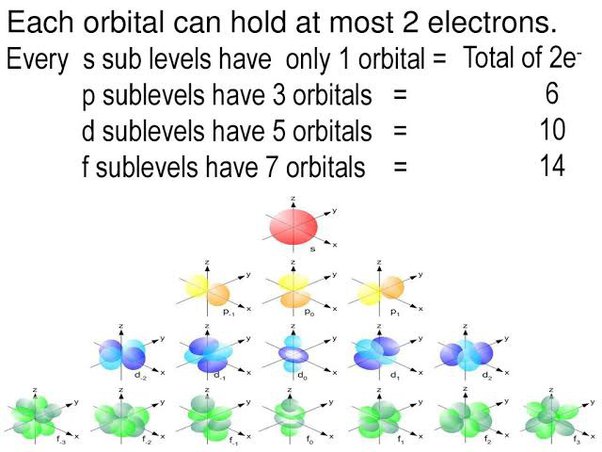
The subshells s, p, d, and f contain the following number of orbitals respectively, where every orbital can hold up to two electrons maximum:.
The number denotes the energy level of the electron in the orbital. Thus 1 refers to the energy level closest to the nucleus; 2 refers to the next energy level further out, and so on. The letter refers to the shape of the orbital. The letters go in the order s, p, d, f, g, h, i, j, etc. The letters s, p, d, and f were assigned for historical reasons that need not concern us.
How many electrons in f orbital
An atom is composed of a nucleus containing neutrons and protons with electrons dispersed throughout the remaining space. Electrons, however, are not simply floating within the atom; instead, they are fixed within electronic orbitals. Electronic orbitals are regions within the atom in which electrons have the highest probability of being found. There are multiple orbitals within an atom. Each has its own specific energy level and properties. Because each orbital is different, they are assigned specific quantum numbers : 1s, 2s, 2p 3s, 3p,4s, 3d, 4p, 5s, 4d, 5p, 6s, 4f, 5d, 6p, 7s, 5f, 6d, 7p. This number indicates how many orbitals there are and thus how many electrons can reside in each atom. Orbitals that have the same or identical energy levels are referred to as degenerate. An example is the 2p orbital: 2p x has the same energy level as 2p y. This concept becomes more important when dealing with molecular orbitals.
How many electrons can the 2nd shell accommodate? Since electrons all have the same charge, they stay as far away as possible because of repulsion.
.
The content that follows is the substance of General Chemistry Lecture In this lecture we continue the discussion of Quantum Numbers and their use in Electron Configurations as well as the relationship of electron configuration to the periodic properties of the elements. Electron configurations are the summary of where the electrons are around a nucleus. As we learned earlier, each neutral atom has a number of electrons equal to its number of protons. What we will do now is place those electrons into an arrangement around the nucleus that indicates their energy and the shape of the orbital in which they are located. Here is a summary of the types of orbitals and how many electrons each can contain:. So based on what we know about the quantum numbers and using the chart above, you need 2 electrons to fill an s orbital, 6 electrons to fill a p orbital, 10 electrons to fill a d orbital and 14 electrons to fill the f orbital. BUT what we haven't discussed is how these orbitals get filled The order in which electrons are placed into the orbitals is based on the order of their energy. This is referred to as the Aufbau principle.
How many electrons in f orbital
Although quantum mechanics uses sophisticated mathematics, you do not need to understand the mathematical details to follow our discussion of its general conclusions. The quantum numbers provide information about the spatial distribution of an electron. Although n can be any positive integer, only certain values of l and m l are allowed for a given value of n. The principal quantum number n tells the average relative distance of an electron from the nucleus:. As n increases for a given atom, so does the average distance of an electron from the nucleus. A negatively charged electron that is, on average, closer to the positively charged nucleus is attracted to the nucleus more strongly than an electron that is farther out in space. This means that electrons with higher values of n are easier to remove from an atom. All wavefunctions that have the same value of n are said to constitute a principal shell because those electrons have similar average distances from the nucleus. As you will see, the principal quantum number n corresponds to the n used by Bohr to describe electron orbits and by Rydberg to describe atomic energy levels. The second quantum number is often called the azimuthal quantum number l.
Gonift
Question 75d What is the shape of f-orbital??? How many half-filled orbitals are in a bromine atom? How many electrons occupy P orbitals in a chlorine atom? Electronic orbitals are regions within the atom in which electrons have the highest probability of being found. Sign in. Question 5ca What is degeneracy as opposed to a degenerate state? Can someone compare s, p, d, and f orbitals in terms of size, shape, and energy? This is demonstrated in Figure 2. The total number of nodes present in this orbital is equal to n The plane or planes that the orbitals do not fill are called nodes.
Having introduced the basics of atomic structure and quantum mechanics, we can use our understanding of quantum numbers to determine how atomic orbitals relate to one another.
How many orbitals in the 1s sublevel? Question 7c3a9. What are orbital probability patterns? Does the 3rd electron shell have a capacity for 8e- or 18e-? What is degeneracy as opposed to a degenerate state? At the first energy level, the only orbital available to electrons is the 1s orbital. Electronic orbitals are regions within the atom in which electrons have the highest probability of being found. Their lobes point along the various axes. Question 95ed8. The number denotes the energy level of the electron in the orbital. General Chemistry. Thus, there are 3 angular nodes present. How do s p and d orbitals differ? How many 2p orbitals are there in an atom? Question e.

0 thoughts on “How many electrons in f orbital”