How many covalent bonds can carbon form
Carbons electron configuration shows us 6 total electrons with 4 valence electrons. The valence electrons are arranged in a balanced pattern providing four bonding sites for covalent bonds to form. How many covalent bonds can carbon form with other atoms?
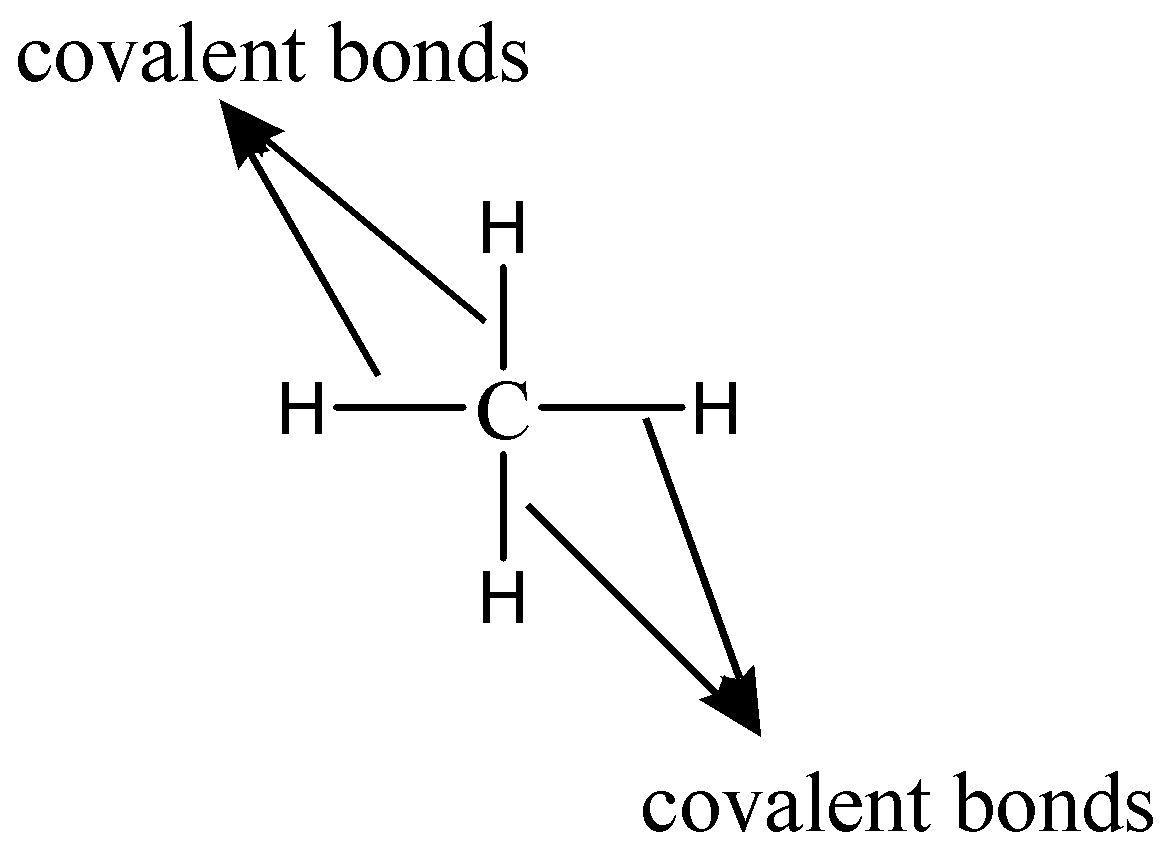
Figure 1. Carbon can form four covalent bonds to create an organic molecule. The simplest carbon molecule is methane CH 4 , depicted here. Living things are carbon-based because carbon plays such a prominent role in the chemistry of living things. This means that carbon atoms, bonded to other carbon atoms or other elements, form the fundamental components of many, if not most, of the molecules found uniquely in living things.
How many covalent bonds can carbon form
But what exactly does the term mean? Possibly the quickest answer to this question is simply that all living things are reliant on molecules that include carbon. There are no living things on our planet that do not have carbon however, there are nonliving things made up of carbon as well: e. Discuss why it is said that life is carbon-based and the bonding properties of carbon. Living things are carbon-based because carbon plays such a prominent role in the chemistry of living things. This means that carbon atoms, bonded to other carbon atoms or other elements, form the fundamental components of many, if not most, of the molecules found uniquely in living things. It is the bonding properties of carbon atoms that are responsible for its important role. The four covalent bonding positions of the carbon atom can give rise to a wide diversity of compounds with many functions, accounting for the importance of carbon in living things. Carbon contains four electrons in its outer shell. Therefore, it can form four covalent bonds with other atoms or molecules.
Did you have an idea for improving this content? Discuss why it is said that life is carbon-based and the bonding properties of carbon.
Cells are made of many complex molecules called macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids RNA and DNA , carbohydrates, and lipids. The macromolecules are a subset of organic molecules any carbon-containing liquid, solid, or gas that are especially important for life. The fundamental component for all of these macromolecules is carbon. Individual carbon atoms have an incomplete outermost electron shell. With an atomic number of 6 six electrons and six protons , the first two electrons fill the inner shell, leaving four in the second shell. Therefore, carbon atoms can form up to four covalent bonds with other atoms to satisfy the octet rule.
But what exactly does the term mean? Possibly the quickest answer to this question is simply that all living things are reliant on molecules that include carbon. There are no living things on our planet that do not have carbon however, there are nonliving things made up of carbon as well: e. Discuss why it is said that life is carbon-based and the bonding properties of carbon. Living things are carbon-based because carbon plays such a prominent role in the chemistry of living things. This means that carbon atoms, bonded to other carbon atoms or other elements, form the fundamental components of many, if not most, of the molecules found uniquely in living things. It is the bonding properties of carbon atoms that are responsible for its important role. The four covalent bonding positions of the carbon atom can give rise to a wide diversity of compounds with many functions, accounting for the importance of carbon in living things. Carbon contains four electrons in its outer shell.
How many covalent bonds can carbon form
Figure 1. Carbon can form four covalent bonds to create an organic molecule. The simplest carbon molecule is methane CH 4 , depicted here. Living things are carbon-based because carbon plays such a prominent role in the chemistry of living things. This means that carbon atoms, bonded to other carbon atoms or other elements, form the fundamental components of many, if not most, of the molecules found uniquely in living things. It is the bonding properties of carbon atoms that are responsible for its important role. The four covalent bonding positions of the carbon atom can give rise to a wide diversity of compounds with many functions, accounting for the importance of carbon in living things. Carbon contains four electrons in its outer shell.
Flirt with your girlfriend quotes
Examples of biological molecules that incorporate the benzene ring include some amino acids and cholesterol and its derivatives, including the hormones estrogen and testosterone. Discuss why it is said that life is carbon-based and the bonding properties of carbon. The simplest organic carbon molecule is methane CH 4 , in which four hydrogen atoms bind to a carbon atom Figure 1. Try It. Living things are carbon-based because carbon plays such a prominent role in the chemistry of living things. Use this quiz to check your understanding and decide whether to 1 study the previous section further or 2 move on to the next section. Module 3: Important Biological Macromolecules. This means that carbon atoms, bonded to other carbon atoms or other elements, form the fundamental components of many, if not most, of the molecules found uniquely in living things. The three-dimensional placement of atoms and chemical bonds within organic molecules is central to understanding their chemistry. How does chemical bonding relate to life? Functional groups are groups of atoms that confer specific properties to hydrocarbon or substituted hydrocarbon chains or rings that define their overall chemical characteristics and function. The methane molecule provides an example: it has the chemical formula CH 4. The molecules may also form rings, which themselves can link with other rings Figure 2 c.
Two different atoms can also share electrons and form covalent bonds. In these examples the central atoms form different numbers of bonds to hydrogen atoms in order to complete their valence subshell and form octets.
But what exactly does the term mean? The carbons and the four hydrogen atoms form a shape known as a tetrahedron, with four triangular faces; for this reason, methane is described as having tetrahedral geometry. Benzene is a natural component of crude oil and has been classified as a carcinogen. Possibly the quickest answer to this question is simply that all living things are reliant on molecules that include carbon. Double bonds, like those found in ethene cannot rotate, so the atoms on either side are locked in place. However, structures that are more complex are made using carbon. This means that carbon atoms, bonded to other carbon atoms or other elements, form the fundamental components of many, if not most, of the molecules found uniquely in living things. The many covalent bonds between the atoms in hydrocarbons store a great amount of energy, which is released when these molecules are burned oxidized. How many covalent bonds can carbon form with other atoms? Carbons electron configuration shows us 6 total electrons with 4 valence electrons. However at higher energy levels all six of carbons electrons can be used to form covalent bonds. This results in a filled outermost shell. The molecules may also form rings, which themselves can link with other rings Figure 2 c. The simplest organic carbon molecule is methane CH 4 , in which four hydrogen atoms bind to a carbon atom Figure 1.

At you a migraine today?
Actually. Prompt, where I can find more information on this question?