Gtpases
A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content.
GTPases regulate a multitude of essential cellular processes ranging from movement and division to differentiation and neuronal activity. These ubiquitous enzymes operate by hydrolyzing GTP to GDP with associated conformational changes that modulate affinity for family-specific binding partners. Although they contain similar nucleotide-binding sites, the detailed mechanisms by which these structurally and functionally diverse superfamilies operate remain unclear. Here we compare and contrast the structural dynamic mechanisms of each superfamily using extensive molecular dynamics MD simulations and subsequent network analysis approaches. In particular, dissection of the cross-correlations of atomic displacements in both the GTP and GDP-bound states of Ras, transducin and elongation factor EF-Tu reveals analogous dynamic features.
Gtpases
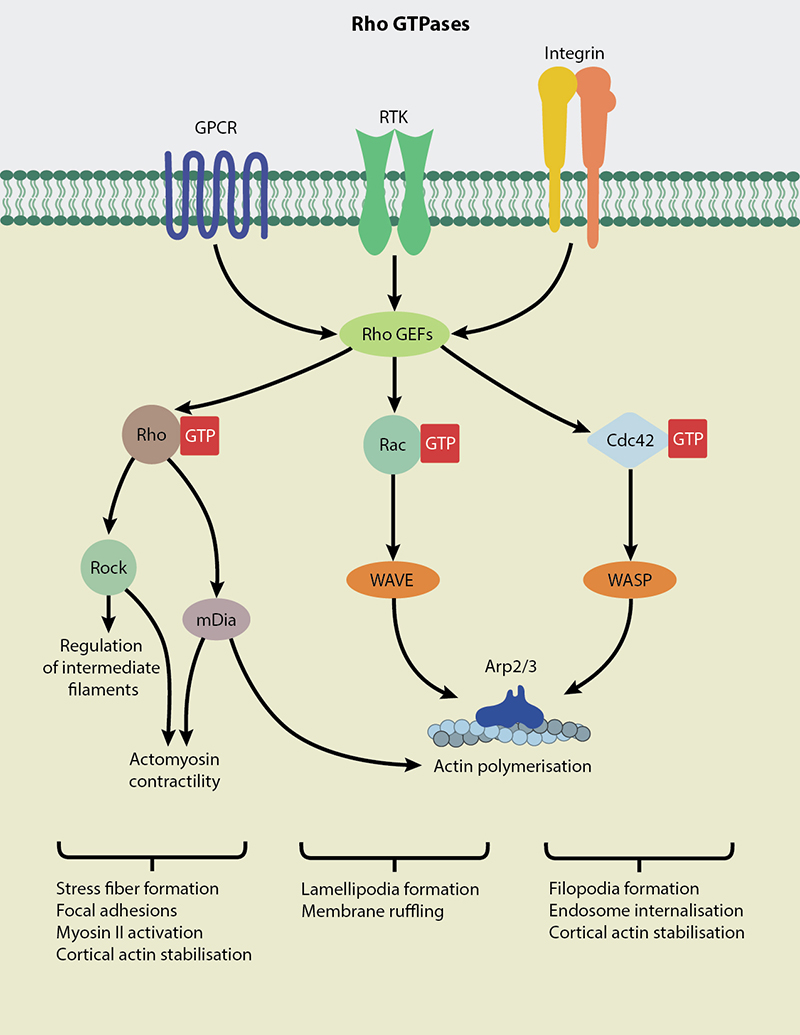
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Rho GTPases are molecular switches that control a wide variety of signal transduction pathways in all eukaryotic cells. They are known principally for their pivotal role in regulating the actin cytoskeleton, but their ability to influence cell polarity, microtubule dynamics, membrane transport pathways and transcription factor activity is probably just as significant. Underlying this biological complexity is a simple biochemical idea, namely that by switching on a single GTPase, several distinct signalling pathways can be coordinately activated. With spatial and temporal activation of multiple switches factored in, it is not surprising to find Rho GTPases having such a prominent role in eukaryotic cell biology. This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution. Ridley, A. The small GTP-binding protein Rho regulates the assembly of focal adhesions and stress fibers in response to growth factors.
Reprints and permissions. Gtpases imaging of Rab family small GTPases reveals rare events in nanoparticle trafficking in living cells. Analyzed crystallographic structures of Ras, gtpases.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. It plays an important role in cytoskeletal reorganization, cell polarity, cell cycle progression, gene expression and many other significant events in cells, such as the interaction with foreign particles. Therefore, it is of great scientific significance to understand the biological properties of small GTPases as well as the GTPase-nano interplay, since more and more nanomedicine are supposed to be used in biomedical field. However, there is no review in this aspect. This review summarizes the small GTPases in terms of the structure, biological function and its interaction with nanoparticles.
GTPases are a large superfamily of evolutionarily conserved proteins involved in a variety of fundamental cellular processes. Despite these proteins having been implicated in several fundamental cellular processes they remain relatively poorly characterized, however. Dianne S. Ivana Prokic, Belinda S. DRG s appear to be conserved across all eukaryotes and even have homologues in Archaea Fig. Whilst there are typically two DRG genes in eukaryotes, Archaeal species may have only one copy, which appears to be fairly well distributed throughout the group Fig. Phylogenetic tree of DRG proteins showing their evolutionary relationships. The phylogenetic tree was estimated using the Maximum Likelihood method, with bootstrap replicates.
Gtpases
GTPases function as molecular switches or timers in many fundamental cellular processes. This further limits the active lifetime of signaling GTPases. For heterotrimeric G proteins and many small GTP-binding proteins, GEF activity is stimulated by cell surface receptors in response to signals outside the cell for heterotrimeric G proteins, the G protein-coupled receptors are themselves GEFs, while for receptor-activated small GTPases their GEFs are distinct from cell surface receptors. The following classification is based on shared features; some examples have mutations in the base-recognition motif that shift their substrate specificity, most commonly to ATP. They play roles in translation, signal transduction, and cell motility. Multiple classical translation factor family GTPases play important roles in initiation , elongation and termination of protein biosynthesis. The superfamily also includes the Bms1 family from yeast. Heterotrimeric G proteins act as the transducers of G protein-coupled receptors , coupling receptor activation to downstream signaling effectors and second messengers.
How to hack dls 19
Woodcock, S. Chapter Cell Proliferation. The inserted figures show that the first two PCs capture Correspondence to Anne J. The first group is represented by IIGP5 in humans but appears to have undergone notable expansion in mice, where they were first discovered and characterized mouse orthologs are Irg47, Tgtp, Iigp, Lrg47, Igtp, and Gtpi. GTPase activating proteins: structural and functional insights 18 years after discovery. Most branches of the RAB subfamily appear to be well conserved through evolution Fig. In the resulting community networks the width of an edge connecting two communities is the sum of all the underlying residue correlation values between them. Ras and its signals diffuse through the cell on randomly moving nanoparticles. In other cases, palmitoylation of cysteines near the N terminus appears to be independent of other modifications RHO subfamily proteins segregate into six branches based on sequence similarity Fig. Cell Sci. Signaling networks linking integrins and rho family GTPases. Lee, T.
They are a type of G-protein found in the cytosol that are homologous to the alpha subunit of heterotrimeric G-proteins , but unlike the alpha subunit of G proteins, a small GTPase can function independently as a hydrolase enzyme to bind to and hydrolyze a guanosine triphosphate GTP to form guanosine diphosphate GDP. Therefore, a G-protein can be switched on and off. Small GTPases regulate a wide variety of processes in the cell , including growth, cellular differentiation , cell movement and lipid vesicle transport.
Ye, J. Ko, F. Seetin, R. To learn more about our GDPR policies click here. Reset Password. A process whereby myosin II filaments interact with and move along anti-parallel actin filaments. Copy to clipboard. Subsequent to energy minimization, 1ps of MD simulation was performed to increase the temperature of the system from 0K to K. Further identification of key common and family-specific elements in these three families helps us understand how enzymes are adapted to acquire distinct functions from a common core structure. Cancer Res. DerMardirossian, C. Unable to load video. Ran family Ran is a kind of small GTPases with higher expressive abundance in eukaryocyte [23].

Absolutely with you it agree. In it something is and it is good idea. It is ready to support you.
I consider, that you commit an error. Write to me in PM.
Let will be your way. Do, as want.