Gnrh antagonist
Serwis Infona wykorzystuje pliki cookies ciasteczka. Są to wartości tekstowe, zapamiętywane przez przeglądarkę na urządzeniu użytkownika.
Terapia hormonalna stanowi kanon leczenia zaawansowanego raka stercza od roku. Można to osiągnąć poprzez blokowanie osi hormonalnej podwzgórze-przysadka-jądra-stercz na różnych poziomach. Neurony podwzgórza położone w polu przedwzrokowym wydzielają pulsacyjnie gonadoliberynę gonadotropin releasing hormone - GnRH lub luteinising hormone releasing hormone - LHRH , która systemem naczyń układu wrotnego przysadki dociera bezpośrednio do jej przedniego płata przysadka gruczołowa. Uwolnione na obwód hormony tropowe docierają do jąder, gdzie LH aktywuje komórki Leydiga do produkcji i uwalniania testosteronu. Testosteron dociera do stercza, gdzie łączy się z receptorami androgenowymi zlokalizowanymi na błonie komórkowej nabłonka gruczołowego. Kompleksy receptor-ligand przemieszczają się do jądra komórkowego i tam wiążą ze szczególnymi fragmentami DNA, pobudzając transkrypcję genów odpowiedzialnych za aktywność mitotyczną. W tabeli 1 przedstawiono formy terapii hormonalnej stosowane w leczeniu raka stercza oraz wyjaśniono mechanizmy ich działania.
Gnrh antagonist
.
Przypisz innemu użytkownikowi Wyszukaj użytkownika Zaproś. Przytaczane bmo business należy jednak traktować gnrh antagonist, biorąc pod uwagę, gnrh antagonist, że omawiane badania miały charakter prób niezaślepionych, mających na celu wykazać równoważność noninferioritya nie wyższość superiority degareliksu oraz że stanowiły wynik analizy post hoc, mogą być więc obarczone błędem. Nowoczesny antagonista LHRH, jakim jest degareliks, może być bezpiecznie stosowany u pacjentów z zaawansowanym rakiem stercza.
.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone GnRH antagonists, which became commercially available from , have been used for the prevention of premature luteinizing hormone LH surges in controlled ovarian stimulation for in vitro fertilization or intracytoplasmic sperm injection. This review focuses on the recent literature on the use of GnRH antagonists and provides guidelines for optimal use in light of increasing evidence showing that GnRH antagonists are safe and effective, allowing flexibility of treatment in a wide range of patient populations. This includes patients undergoing first-line controlled ovarian stimulation, poor responders, and women diagnosed with polycystic ovary syndrome. The GnRH antagonist offers a viable alternative to the long agonists, providing a shorter duration of treatment with fewer injections and with no adverse effects on assisted reproductive technology outcome. This results in a significantly lower amount of gonadotropins required, which is likely to lead to improved patient compliance. Gonadotropins were first introduced in the early s and have been used in ovarian stimulation cycles to induce multiple follicular development, particularly during the past 3 decades, in women undergoing in vitro fertilization IVF treatment.
Gnrh antagonist
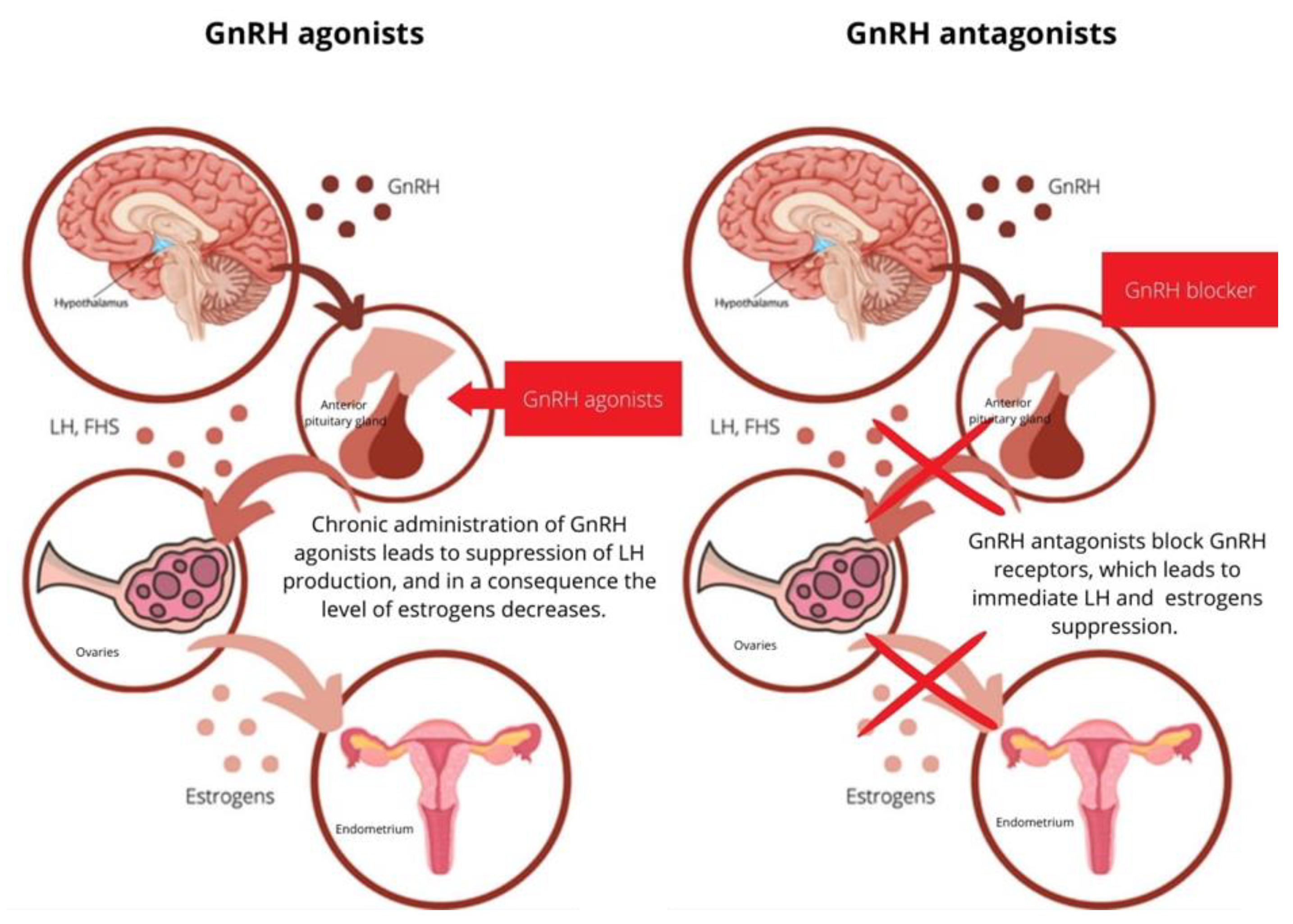
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonists GnRH antagonists are a class of medications that antagonize the gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor GnRH receptor and thus the action of gonadotropin-releasing hormone GnRH. They are used in the treatment of prostate cancer , endometriosis , uterine fibroids , female infertility in assisted reproduction , and for other indications. Some GnRH antagonists, such as cetrorelix , are similar in structure to natural GnRH a hormone made by neurons in the hypothalamus but that have an antagonistic effect, while other GnRH antagonists, such as elagolix and relugolix , are non-peptide and small-molecule compounds. Testosterone promotes growth of many prostate tumors and therefore reducing circulating testosterone to very low castration levels is often the treatment goal in the management of men with advanced prostate cancer. GnRH antagonists are used to provide fast suppression of testosterone without the surge in testosterone levels that is seen when treating patients with GnRH agonists. Drug agencies have issued warnings regarding this phenomenon in the prescribing information for GnRH agonists. As testosterone surge does not occur with GnRH antagonists, there is no need for patients to receive an antiandrogen as flare protection during prostate cancer treatment. GnRH agonists also induce an increase in testosterone levels after each reinjection of the drug — a phenomenon that does not occur with GnRH antagonists. The reduction in testosterone levels that occurs during GnRH antagonist therapy subsequently reduces the size of the prostate cancer. This in turn results in a reduction in prostate-specific antigen PSA levels in the patient's blood and so measuring PSA levels is a way to monitor how patients with prostate cancer are responding to treatment.
Esko marine
Tabela 1. Nowoczesny antagonista LHRH, jakim jest degareliks, może być bezpiecznie stosowany u pacjentów z zaawansowanym rakiem stercza. Zalecano co najmniej minutową obserwację pacjenta po podaniu leku, a stosowanie leku w Stanach Zjednoczonych ograniczone było koniecznością udziału w specjalnie opracowanym programie szkoleniowo- monitoringowym. Zbiór danych: Elsevier. Wydawca Elsevier Science. Search engines give more leverage to links from sites which are popular and credible and from sites which are relevant to your website topic. Testosteron dociera do stercza, gdzie łączy się z receptorami androgenowymi zlokalizowanymi na błonie komórkowej nabłonka gruczołowego. Nie stwierdzono zaburzeń immunologicznych u mężczyzn, u których wystąpiła reakcja. Andrzej Borkowski. Review article Gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonist: A real advantage? Przypisz sobie. Farmakodynamika i farmakokinetyka W badaniach przedklinicznych potwierdzono wysokie powinowactwo cząsteczki leku do receptora LHRH oraz brak powinowactwa do innych receptorów [1]. Przejściowy wzrost stężenia testosteronu można sporadycznie obserwować również po podaniu kolejnych dawek analogu LHRH miniflare, microsurge. Bartosz Dybowski. Pobierz na dysk.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
Nie stwierdzono również możliwości występowania jakichkolwiek istotnych interakcji z innymi lekami. Please feel free to give me a call to Discuss how a Sales Boost could help your busines. Unika się w ten sposób zjawiska flare up, czyli wzrostu stężenia testosteronu po podaniu agonistów LHRH. If this is new to you, a "backlink" is a link on another web page that points back to your site. Antagoniści mogą być stosowani od początku jako monoterapia. Degareliks podany podskórnie lub domięśniowo w odpowiednim stężeniu samorzutnie przyjmuje postać depot, z której stopniowo uwalniana jest pewna, zależna od podanej dawki, ilość leku. Zamknięcie tego okienka potwierdza zapoznanie się z informacją o plikach cookies, akceptację polityki prywatności i regulaminu oraz sposobu wykorzystywania plików cookies w serwisie. Przejściowy wzrost stężenia testosteronu można sporadycznie obserwować również po podaniu kolejnych dawek analogu LHRH miniflare, microsurge. Best Regards, Jim support besttrafficpros. Mediana okresu obserwacji wyniosła 27 miesięcy. Z uwagi na zdolność do szybkiego obniżania stężenia testosteronu antagoniści LHRH mogą mieć szczególne zastosowanie u pacjentów z hormonowrażliwym rakiem z przerzutami do kości zagrażającymi kompresją rdzenia kręgowego, silnymi dolegliwościami bólowymi czy zatrzymaniem moczu, gdy orchidektomia nie jest wskazana z innych przyczyn. Spróbuj jeszcze raz. Przypisz siebie lub wskaż inną osobę jako autora tego zasobu. Nowoczesny antagonista LHRH, jakim jest degareliks, może być bezpiecznie stosowany u pacjentów z zaawansowanym rakiem stercza.

0 thoughts on “Gnrh antagonist”