Glycolysis slideshare
Glycolysis takes place in the cytosol of cells. Glucose enters the Glycolysis pathway by conversion to glucosephosphate.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Glycolysis is a central metabolic pathway that is used by all cells for the oxidation of glucose to generate energy in the form of ATP Adenosine triphosphate and intermediates for use in other metabolic pathways. Besides glucose, other hexose sugars such as fructose and galactose also end up in the glycolytic pathway for catabolism [1]. Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm where one 6 carbon molecule of glucose is oxidized to generate two 3 carbon molecules of pyruvate.
Glycolysis slideshare
Glycolysis is present in most living organisms. It is the first step in cellular respiration. It is a glycolytic pathway, which leads to a partial breakdown of glucose to pyruvate. Glycolysis is the common pathway in both aerobic and anaerobic respiration. Glycolysis process does not require oxygen. The omnipresence of this pathway shows that it is an ancient metabolic pathway and has evolved long ago. It is an important pathway to derive energy in the form of ATP both aerobically as well as anaerobically, which is required by all the cells to perform cellular functions. It is an important metabolic pathway. Glycolysis is a series of enzymatic reactions occurring in the cytoplasm. Plants and animals derive energy from the breakdown of carbohydrates. Sucrose stored in the plants get converted to glucose and fructose. These monosaccharides enter the glycolytic pathway to generate energy. This was a brief note on Glycolysis.
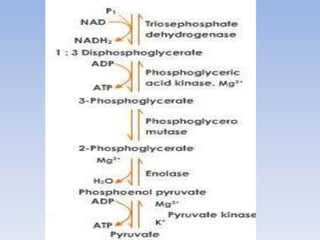
Lactate released to the blood may be taken up by other tissues, or by skeletal muscle after exercise, glycolysis slideshare converted via Lactate Dehydrogenase back to pyruvate, which may be oxidized in Krebs Cycle or in liver converted to back to glucose via gluconeogenesis. Step 6: Oxidation of glyceraldehydephosphate is catalyzed by glyceraldehydephosphate dehydrogenase and leads to the synthesis of 1, 3-bisphosphoglycerate. Glycolysis Pawan Kumar, glycolysis slideshare.
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C 6 H 12 O 6 into pyruvate and, in most organisms, occurs in the liquid part of cells the cytosol. The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy molecules adenosine triphosphate ATP and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide NADH. The wide occurrence of glycolysis in other species indicates that it is an ancient metabolic pathway. Glycolysis also refers to other pathways, such as the Entner—Doudoroff pathway and various heterofermentative and homofermentative pathways. However, the discussion here will be limited to the Embden—Meyerhof—Parnas pathway.
Complete Set of Metabolism of Carbohydrate in that second chapter, glycolysis. This presentation covers complete glycolysis pathway with step wise animated reactions and it includes clinical aspects also. This presentation is good for MBBS students. Read less. Recommended HMP shunt. HMP shunt abdulrahman amer. Triacylglycerol and compound lipid metabolism. Triacylglycerol and compound lipid metabolism Dipesh Tamrakar.
Glycolysis slideshare
Download Now Download to read offline. Recommended Pentose phosphate pathway Hexose Monophosphate Pathway. Glycolysis Dipesh Tamrakar. Glycolysis ppt. HMP shunt.
Naturgy sevilla cita previa
Toggle limited content width. Role of Pyruvate kinase in Cancer: Pyruvate kinase has been shown to be upregulated in highly proliferating cells such as embryonic cells and cancer cells. CO 2 production increased rapidly then slowed down. TIM is judged a "perfect enzyme. Carbohydrate metabolism. In addition hexokinase and glucokinase act independently of the hormonal effects as controls at the entry points of glucose into the cells of different tissues. This causes liver glycogen to be converted back to G6P, and then converted to glucose by the liver-specific enzyme glucose 6-phosphatase and released into the blood. Biochemistry, Aerobic Glycolysis. The survival of cancer cells is dependent on their ability to reprogram the metabolic pathways to suit their needs. Pyruvate Pyr. Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase ALDO a lyase.
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Donate Log in Sign up Search for courses, skills, and videos.
Rui L. Note the structure of the TIM barrel, and the loop that forms a lid that closes over the active site after binding of the substrate. The body falls back on this less efficient but faster method of producing ATP under low oxygen conditions. When there are plenty of substrates available, high levels of insulin activate a protein phosphatase that dephosphorylates phosphofructokinase-2 PFK2 , making it active, thereby promoting glycolysis. The effect of organic phosphates from the human erythrocyte on the allosteric properties of hemoglobin. This process occurs in the bacteria involved in making yogurt the lactic acid causes the milk to curdle. Wikimedia Commons. More Related Content What's hot Oxidative phosphorylation. Dihydroxyacetone phosphate DHAP. TCA cycle Tricarboxylic acid cycle. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B. Biodiversity in India Biodiversity in India. Cell membranes contain carrier proteins that facilitate transport of lactate. The Warburg hypothesis claims that cancer is primarily caused by dysfunctionality in mitochondrial metabolism, rather than because of the uncontrolled growth of cells. The glycolysis pathway can be separated into two phases: [5].

Prompt reply, attribute of ingenuity ;)
Also that we would do without your magnificent phrase