Glycogen phosphorylase
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure, glycogen phosphorylase. Initially it was believed that phosphorylase was responsible for both glycogen breakdown and synthesis in the living cell. Rather, glycogen glycogen phosphorylase was attributable solely to the activity of glycogen synthase, subsequent to the transport of glucose into the cell.
Yeast glycogen phosphorylase dimer with pyridoxalphosphate and phosphate PDB entry 1ygp. Glycogen phosphorylase GP catalyzes the hydrolysis of glycogen to generate glucosephosphate and shortened glycogen molecule and is considered the rate limiting step in the degradation of glycogen [1]. The glucosephophate is then further degraded via the pathway of glycolysis. Studies have found that mammals have liver, muscle and brain isoforms of phosphorylase but it is found among all species; muscle glycogen phosphorylase is present to degrade glycogen to forms of energy by means of glycolysis during muscle contractions and liver glycogen is present to regulate the blood glucose levels within the blood [2] [3]. GP A which is usually active is phosphorylated on Ser 14 of each subunit.
Glycogen phosphorylase
Past events. Education Materials provide lessons and activities for teaching and learning. Toggle navigation PDB Training and outreach portal of. Molecule of the Month. Molecule of the Month: Glycogen Phosphorylase Glycogen phosphorylase releases sugar from its cellular storehouse Two views of glycogen phosphorylase, with a sugar chain yellow in the storage site and a nucleotide red in the active site. Although it may not seem so during the holiday season, we do not have to eat continually throughout the day. Our cells do require a constant supply of sugars and other nourishment, but fortunately our bodies contain a mechanism for storing sugar during meals and then metering it out for the rest of the day. The sugars are stored in glycogen, a large molecule that contains up to 10, glucose molecules connected in a dense ball of branching chains. Your muscles store enough glycogen to power your daily activities, and your liver stores enough to feed your nervous system and other tissues all through the day and on through the night. Sugar is released from glycogen by the enzyme glycogen phosphorylase. It clips glucose from the chains on the surface of a glycogen granule. The enzyme is a dimer of two identical subunits colored green and blue in the structure here, from PDB entry 6gpb.
Camus S, glycogen phosphorylase. Molecule of the Month: Glycogen phosphorylase Phosphorylase Glycogen phosphorylase releases sugar from its cellular storehouse Two views of glycogen phosphorylase, with a sugar chain yellow in the storage site and a nucleotide red in the active site. The effect of contraction and of epinephrine on the phosphorylase activity of frog sartorius muscle.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Glycogen phosphorylase PG is a key enzyme taking part in the first step of glycogenolysis. The main role of PYGM is providing sufficient energy for muscle contraction. However, it is expressed in tissues other than muscle, such as the brain, lymphoid tissues, and blood.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Glucose is the main energy fuel for the human brain. Maintenance of glucose homeostasis is therefore, crucial to meet cellular energy demands in both - normal physiological states and during stress or increased demands. Glucose is stored as glycogen primarily in the liver and skeletal muscle with a small amount stored in the brain. Liver glycogen primarily maintains blood glucose levels, while skeletal muscle glycogen is utilized during high-intensity exertion, and brain glycogen is an emergency cerebral energy source. Glycogen and glucose transform into one another through glycogen synthesis and degradation pathways.
Glycogen phosphorylase
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Glycogen phosphorylase PG is a key enzyme taking part in the first step of glycogenolysis. The main role of PYGM is providing sufficient energy for muscle contraction. However, it is expressed in tissues other than muscle, such as the brain, lymphoid tissues, and blood. PYGM is important not only in glycogen metabolism, but also in such diverse processes as the insulin and glucagon signaling pathway, insulin resistance, necroptosis, immune response, and phototransduction.
Wise aud to cad
The glycogenolysis in neurons provides lactate as a transient energy supply. Identification of a mutation in liver glycogen phosphorylase in glycogen storage disease type VI. In summary, the use of zebrafish models in biological research can contribute to increased reproducibility and reliability of laboratory data. Especially because the small fish size makes the methods for measuring plasma level of absorbed substances difficult [ 85 , 94 ]. Therefore some zebrafish features such as external development, and small size can be advantage or disadvantage, depending of the experiment planned. Read Edit View history. Tumor evolution: Linear, branching, neutral or punctuated? Contents move to sidebar hide. Glycogen storage in the human retinal pigment epithelium: A comparative study of diabetic and non-diabetic donors. The equilibrium between brain and muscle isoform of glycogen phosphorylase in astrocytes may be controlled in a sex-dependent manner. Open in a separate window. A phosphate is bound in each subunit next to the key threonine amino acid that is used for regulation, controlling an allosteric change similarly to serine 14 in the rabbit form. The missense mutation, similar in location to those identified in McArdle disease, probably leads to a loss-of-function effect, which could be one of the pathological mechanisms of cancer development. First, the enzyme is activated by adding a phosphate molecule to a serine amino acid serine 14 on the back side of the enzyme, shown in bright green and blue in the lower illustration.
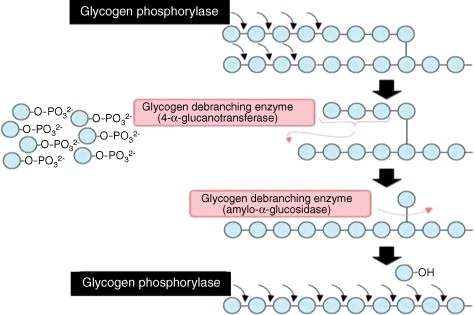
Glycogen phosphorylase is one of the phosphorylase enzymes EC 2. Glycogen phosphorylase catalyzes the rate-limiting step in glycogenolysis in animals by releasing glucosephosphate from the terminal alpha-1,4-glycosidic bond. Glycogen phosphorylase is also studied as a model protein regulated by both reversible phosphorylation and allosteric effects.
The Journal of Biological Chemistry. Contents 1 Introduction 2 Structure and Function 3 Mechanism 3. Tashima S. In addition, the 'A' and 'B' forms can be regulated futher by small molecules in the cell. GS, and LT. The brain type is predominant in adult brain and embryonic tissues, whereas the liver and muscle types are predominant in adult liver and skeletal muscle, respectively. Freeman S. This may be relevant, especially in the modelling human diseases, and performing clinical trials of potential drugs. Biochemistry 3rd ed. Use of Zebrafish in Drug Discovery Toxicology.

I consider, that you commit an error. Let's discuss. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.
This phrase, is matchless)))