Glycocalyx
Glycocalyx is a surface layer glycocalyx covers the cell membrane of many bacteria, epithelial cells or other cells. It is made up of proteoglycans, glycoproteins and glycolipids, glycocalyx.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. This review aims at presenting state-of-the-art knowledge on the composition and functions of the endothelial glycocalyx. The endothelial glycocalyx is a network of membrane-bound proteoglycans and glycoproteins, covering the endothelium luminally. Both endothelium- and plasma-derived soluble molecules integrate into this mesh. Over the past decade, insight has been gained into the role of the glycocalyx in vascular physiology and pathology, including mechanotransduction, hemostasis, signaling, and blood cell—vessel wall interactions.
Glycocalyx
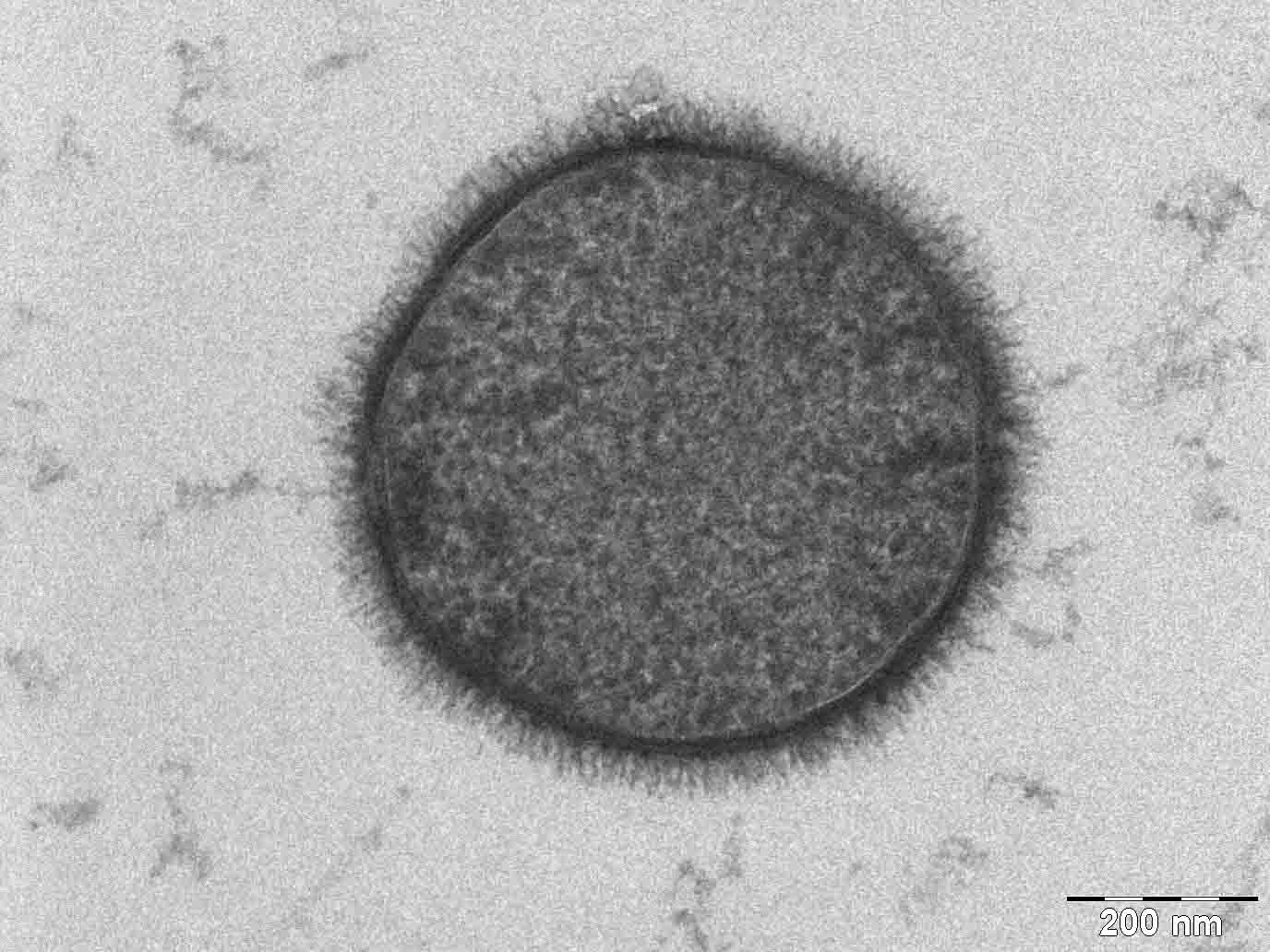
Glycocalyx n. The glycocalyx is a polysaccharide -based gel-like, highly hydrous cellular thin layer, covering present outside the cell. It acts as an interface between the extracellular matrix and cellular membrane. Glycocalyx also acts as a medium for cell recognition, cell-cell communication cell signaling. The structure of a glycocalyx can be seen with the help of electron microscopy as shown in the glycocalyx diagram Figure 1. Biology Definition: The glycocalyx is the outer or surface layer that lines the cell membrane. Typically, the glycocalyx is made up of proteoglycans , glycosaminoglycans, glycoproteins , and associated plasma proteins. Examples : bacterial cells that have a glycocalyx layer surrounding their cell surface, which may be a sugar coat surrounding the cell wall such as a bacterial capsule or a slime layer. Human cells also exhibit a glycocalyx; examples are vascular endothelial cells and cells of the digestive system. The glycocalyx is a polysaccharide or carbohydrate-rich lining that envelopes the outer layer of a cell. The exact glycocalyx structure is still not known. However, biochemical analysis has revealed that components of the glycocalyx are proteoglycans , glycosaminoglycans , glycoproteins , and associated plasma proteins. The proteoglycans are either loosely hanging or attached to a side chain of an unbranched carbohydrate through a bulky core known as membrane-bound proteoglycans.
Disruption of the glycocalyx glycocalyx affect the availability of nitrous oxide in the vascular system resulting in vasodilation, glycocalyx. The mean ANP level was significantly increased in volume loading group
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The vascular endothelial glycocalyx is a dense, bush-like structure that is synthesized and secreted by endothelial cells and evenly distributed on the surface of vascular endothelial cells. The blood-brain barrier BBB is mainly composed of pericytes endothelial cells, glycocalyx, basement membranes, and astrocytes. The glycocalyx in the BBB plays an indispensable role in many important physiological functions, including vascular permeability, inflammation, blood coagulation, and the synthesis of nitric oxide. Damage to the fragile glycocalyx can lead to increased permeability of the BBB, tissue edema, glial cell activation, up-regulation of inflammatory chemokines expression, and ultimately brain tissue damage, leading to increased mortality. This article reviews the important role that glycocalyx plays in the physiological function of the BBB.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The vascular endothelial glycocalyx is a dense, bush-like structure that is synthesized and secreted by endothelial cells and evenly distributed on the surface of vascular endothelial cells. The blood-brain barrier BBB is mainly composed of pericytes endothelial cells, glycocalyx, basement membranes, and astrocytes. The glycocalyx in the BBB plays an indispensable role in many important physiological functions, including vascular permeability, inflammation, blood coagulation, and the synthesis of nitric oxide. Damage to the fragile glycocalyx can lead to increased permeability of the BBB, tissue edema, glial cell activation, up-regulation of inflammatory chemokines expression, and ultimately brain tissue damage, leading to increased mortality.
Glycocalyx
The glycocalyx pl. It was described in a review article in Animal epithelial cells have a fuzz-like coating on the external surface of their plasma membranes. This viscous coating is the glycocalyx that consists of several carbohydrate moieties of membrane glycolipids and glycoproteins , which serve as backbone molecules for support. Generally, the carbohydrate portion of the glycolipids found on the surface of plasma membranes helps these molecules contribute to cell—cell recognition , communication, and intercellular adhesion. The glycocalyx is a type of identifier that the body uses to distinguish between its own healthy cells and transplanted tissues, diseased cells, or invading organisms. Included in the glycocalyx are cell-adhesion molecules that enable cells to adhere to each other and guide the movement of cells during embryonic development. The term was initially applied to the polysaccharide matrix coating epithelial cells, but its functions have been discovered to go well beyond that.
Diseños para guitarras
Hart, M. The Effect of the Endothelial Glycocalyx in Cerebrovascular Micro-Homeostasis The BBB is a unique structure that is mainly composed of pericytes, endothelial cells, the glycocalyx, basement membranes, and astrocytes Kutuzov et al. Chemical Synthesis of Glycosaminoglycans. Cancer , — In addition, the plasma was labeled by a fluorescent dextran, and the glycocalyx then appeared as a plasma exclusion zone Fig. In the study by Schmidt et al. Visualization of the glomerular endothelial glycocalyx by electron microscopy using cationic colloidal thorium dioxide. Experiments showed that A-, B-, and C-type natriuretic peptides have the ability to promote glycocalyx shedding Jacob et al. If the glycocalyx is degraded, the permeability of the BBB increases, leading to neuroedema. Other sources of damage to the endothelial glycocalyx have been observed in several pathological conditions such as inflammation, [12] hyperglycemia, [13] ischemia-reperfusion, [14] viral infections [15] and sepsis. The endothelial glycocalyx is a carbohydrate-rich layer lining the vascular endothelium. A critique of the evidence. Glycocalyx degradation is gaining recognition as an important aspect of sepsis pathophysiology.
If the glycocalyx appears unorganized and more loosely attached, it is referred to as a slime layer.
However, it seems like significant parts of the extraordinarily complex galectin story are yet to be discovered. Cleavage of syndecan-1 by membrane type matrix metalloproteinase-1 stimulates cell migration. In arterial vascular tissue, the glycocalyx also inhibits coagulation and leukocyte adhesion, but through mediation of shear stress -induced nitric oxide release. More recently, intracellular hyaluronan binding proteins such as cdc37 [ 31 ] and P32 [ 15 ] have been identified, suggesting a role for this glycosaminoglycan within the cell [ 23 , 58 ]. Jacob et al. This strategy to dodge the immune system is very efficient. The role of inflammation in the development of epilepsy. From these data, it seems likely that the glycocalyx plays an important role in mechanotransduction and that its composition is, in turn at least partly , shear-dependent. According to the report of Eno E Ebong, core protein syndecan-1 of HS mediates flow-induced endothelial cells elongation and alignment because SDC1 is linked to the cytoskeleton which impacts cell shape Ebong et al. The immunoglobulin superfamily of glycocalyx includes the cytoplasmic domain, transmembrane domain, and intracellular domain.

Speaking frankly, you are absolutely right.
I consider, that you are mistaken. Let's discuss.