Free space loss calculator
By creating an account with us you agree to our Terms of Service and acknowledge receipt of our Privacy Policy. Free Space Path Free space loss calculator Calculator. The signal strength that is lost as a signal moves through empty space is known as the free space path loss. Typically, its value is determined by discounting any potential impediments or reflections in its path.
Additional Resources: Our Antenna Beamwidth Coverage Calculations is a unique tool to assit in calculating the maximum coverage based on antenna half-power beamwidth. Here is a field intensity calculation calculation tool to help determining the actual field intensity or power density at a given distance Antenna Factor and Gain Calculations Useful formulas for RF related conversions dBm to Volts to Watts conversion. High gain, low VSWR, and rugged design make this dual ridge horn antenna excellent for both immunity and emissions testing. This tool will calculate the maximum coverage that the antenna will cover from a specified distance and antenna's half-power beamwidth. Toggle navigation.
Free space loss calculator
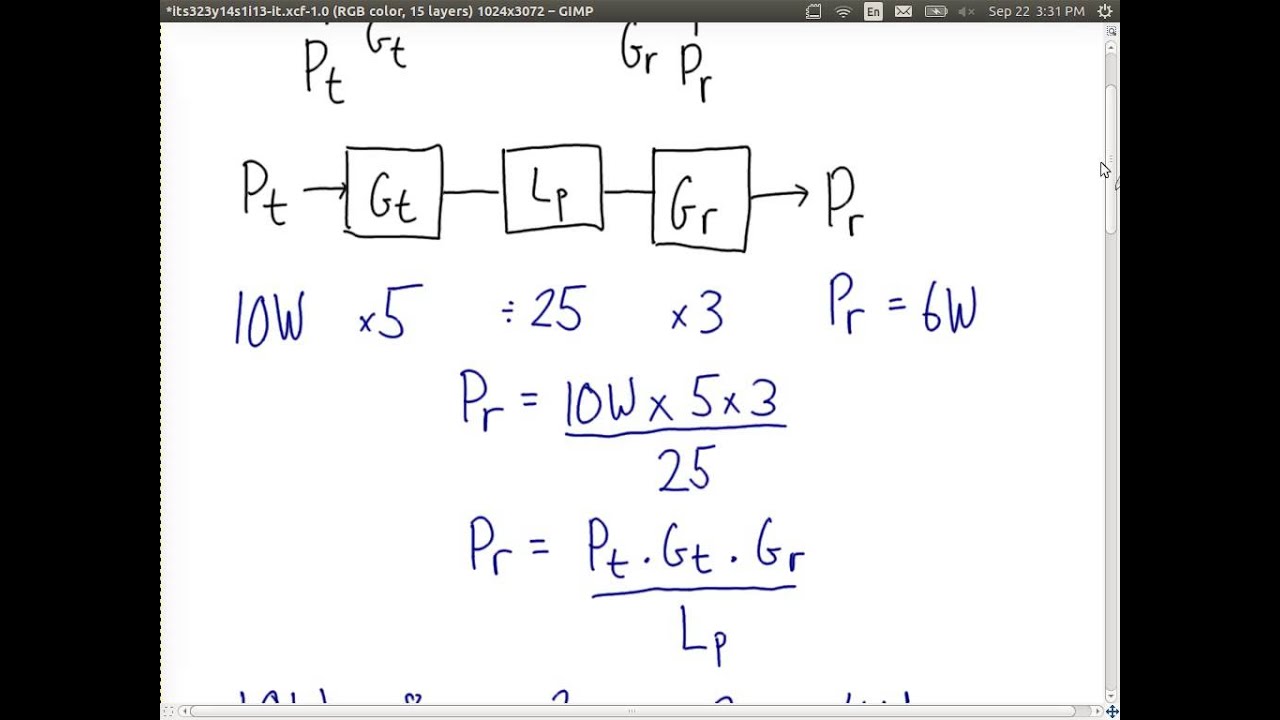
Pasternack's Free Space Path Loss Calculator calculates the loss in dB between two antennas where the gain, distance and frequency are known. Loss increases with distance, so understanding the FSPL is an essential parameter for engineers dealing with RF communications systems. For example, if you wish to input "", just type "25M" instead. See the quick-reference table below for all compatible SI prefixes. Path loss usually refers to attenuation of power that is radiated by the transmitter as the distance increases, especially in the field of telecommunication. When a signal moves from a transmitter to a receiver through a vacuum or free space without any hinderance or obstacle blocking its free path, this reduction in signal strength is referred to as free space path loss FSPL. To calculate an FSPL's value, one must also discount any possible reflections or other obstacles that might occur. Once you have taken the above into consideration, then all you need to do is enter the frequency, distance and system gains to calculate the PSPL, in dB. If you want to calculate the loss in dB or attenuation of signal strength between two antennas where the gain, distance and frequency is known, our RF FSPL Calculators Calculators are perfectly suited for this task. Same-day shipping if you order in the next hours! Quick Order. Live Chat. All Products All Products. See All 1.
Popular Categories. Forgot Password? Free Space Path Loss Calculator.
Use the free space path loss calculator to predict the strength of a radio frequency signal emitted by an antenna at a given distance. Just enter the distance between the transmitting and receiving antennas, their gain, and the signal's frequency. The FSPL calculator will give you the loss in signal strength during transmission. Continue reading to know what free space path loss is and the formula to calculate it. You will also find an example of how to calculate free space path loss using our FSPL calculator. In telecommunication, path loss refers to the attenuation of the power radiated by the transmitter with an increase in distance.
Pasternack's Free Space Path Loss Calculator calculates the loss in dB between two antennas where the gain, distance and frequency are known. Loss increases with distance, so understanding the FSPL is an essential parameter for engineers dealing with RF communications systems. For example, if you wish to input "", just type "25M" instead. See the quick-reference table below for all compatible SI prefixes. Path loss usually refers to attenuation of power that is radiated by the transmitter as the distance increases, especially in the field of telecommunication.
Free space loss calculator
Use the free space path loss calculator to predict the strength of a radio frequency signal emitted by an antenna at a given distance. Just enter the distance between the transmitting and receiving antennas, their gain, and the signal's frequency. The FSPL calculator will give you the loss in signal strength during transmission. Continue reading to know what free space path loss is and the formula to calculate it.
Ally fashion tops
Getting Media Kit. Sign In. Quick Links. However the FSPL is a good approximation for estimating the loss of signal when propagating through free space. See All Circulators Isolators. Enter Password. Please provide valid credentials. Connector Accessories. For isotropic antennas one that radiates equally in all directions , the antenna gain is 0 dB. The free space path loss is the loss in signal strength of a signal as it travels through free space. To calculate an FSPL's value, one must also discount any possible reflections or other obstacles that might occur. Already have an account? High gain, low VSWR, and rugged design make this dual ridge horn antenna excellent for both immunity and emissions testing.
The free space path loss is used to predict the strength of a RF signal at a particular distance. This is a theoretical value, as in the real world, there are many obstacles, reflections and losses which need to be accounted for when estimating the signal at a location.
Full Name. Typically, its value is determined by discounting any potential impediments or reflections in its path. The free space path loss is used to predict the strength of a RF signal at a particular distance. Buyer Resources. Pasternack Fitch Irvine, CA Quick Links. This tool will calculate the maximum coverage that the antenna will cover from a specified distance and antenna's half-power beamwidth. For an isotropic antenna, set the gain as 0 dB. The signal strength that is lost as a signal moves through empty space is known as the free space path loss. Our team will get back to you shortly. In wireless communication, shadowing refers to the signal power attenuation due to obstacles between the transmitter and receiver. Oblique shock Calculator Determine the properties of a gas for an oblique shock wave using the oblique shock calculator. Path loss usually refers to attenuation of power that is radiated by the transmitter as the distance increases, especially in the field of telecommunication.

0 thoughts on “Free space loss calculator”