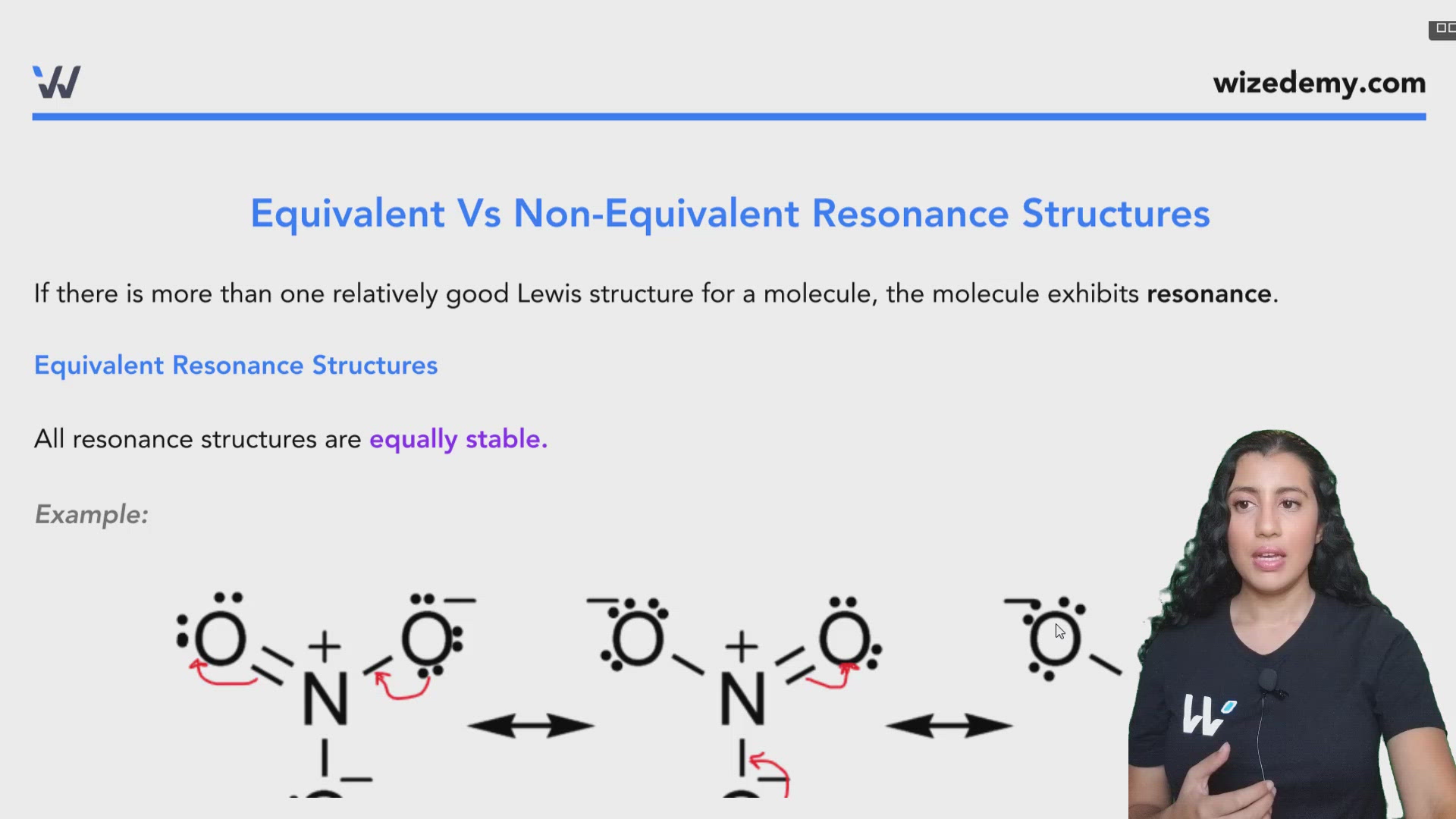
Equivalent resonance structures
Lewis formulas are misleading in the sense that atoms and electrons are shown as being static.
Revolutionized is reader-supported. When you buy through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commision. Learn more here. Chemists must know about equivalent resonance structures in their work. What are they, and why does it matter? Before getting into equivalent resonance structures, people must understand Lewis structures. They also indicate the bonds between atoms.
Equivalent resonance structures
A resonance form is another way of drawing a Lewis dot structure for a given compound. Equivalent Lewis structures are called resonance forms. They are used when there is more than one way to place double bonds and lone pairs on atoms. Resonance structures arise when there are more than one way to draw a Lewis dot diagram that satisfies the octet rule. Remember the octet rule is where the atom gains, loses, or shares electrons so that the outer electron shell has eight electrons. We draw them when one structure does not accurately show the real structure. There are some basic principle on the resonance theory. First resonance structures are not real, they just show possible structures for a compound. Resonance structures are not in equilibrium with each other. Resonance structures are not isomers. Isomers have different arrangement of both atoms and electrons.
From the examples given so far it can be seen that some resonance forms are structurally equivalent and others are not.
In cases in which more than one reasonable plausible Lewis structure can be drawn for a species, these structures are called resonance structures or resonance contributors. Resonance structures can be either equivalent or non-equivalent. However, they are not really identical or the same , they are just equivalent. Each structure is called a resonance structure, and they can be connected by the double-headed resonance arrow. There are three equivalent resonance structures for CO 3 2- , and the actual structure of CO 3 2- is a hybrid of the three resonance contributors. Since the resonance structures are equivalent, they are all in the same level of energy and have the same stability, so they make the same contributions to the actual structure of CO
The Resonance stabilization effect also known as the resonance effect , as briefly mentioned in Section 1. The discussion of the resonance effect heavily relies on the understanding of resonance structures. Here, we will focus on how to draw resonance structures or resonance contributors for organic chemistry species and how to compare the relative stabilities between the structures. According to the resonance effect , the greater the number of resonance contributors, the greater the resonance stabilization effect, and the more stable the species is. Some very important rules need to be followed for such purposes. Guidelines for Drawing Resonance Structures:. The way to use curved arrows to show electron transfer is also called arrow pushing , and it is a very important fundamental skill you need to master in organic chemistry. The two resonance structures here are equivalent.
Equivalent resonance structures
Lewis formulas are misleading in the sense that atoms and electrons are shown as being static. By being essentially two-dimensional representations they also fail to give an accurate idea of the three-dimensional features of the molecule, such as actual bond angles and topography of the molecular frame. Furthermore, a given compound can have several valid Lewis formulas. For example CH 3 CNO can be represented by at least three different but valid Lewis structures called resonance forms, or resonance structures , shown below. However, a stable compound such as the above does not exist in multiple states represented by structures I, or II, or III.
How to beat minor test of strength
The actual structure of the carbonate anion is a combination of all three equivalent resonance structures, which can be called a hybrid. Common Examples Benzene is commonly seen in Organic Chemistry and it has a resonance form. Draw all the equivalent resonance structures for following species. But chemists are also interested in how chemicals might help the problem. In this case, it happens to be less stable than the other two and therefore does not make a significant contribution to the hybrid. Include any non-zero formal charges in the structures. Recent Articles. We draw them when one structure does not accurately show the real structure. Double-headed arrows indicate resonance structures that do not exist by themselves. Elsewhere, researchers from Ohio State University developed an artificial intelligence tool that can dramatically shorten drug discovery time frames. The reader must know the flow of the electrons. This structure is less stable and its contribution to the hybrid is probably minor. Another important factor that increases potential energy lowers stability is the presence of atoms with an incomplete octet.
Looking at the structure of formaldehyde we can see that there is a double bond between the central carbon atom and the oxygen atom giving a CO bond order of two. The carbon is singly bonded to each hydrogen atom, which would give each CH bond orders of one.
Notice that there is no formal charge on carbon, since it has no surplus or deficit of valence electrons. The structure shown below is structurally different from the ones shown above. The total number of electrons in the molecule do not change and neither do the number of paired and unpaired electrons. Resonance structures can also be non-equivalent. The total number of valence electrons being shared for all atoms is 4 from carbon and 3 from the three hydrogens, for a total of 7. The tail of the arrow begins at the electron source and the head points to where the electron will be. Double-headed arrows indicate resonance structures that do not exist by themselves. In this case, it happens to be less stable than the other two and therefore does not make a significant contribution to the hybrid. Figure 1. Move lone pair electrons toward a pi bond and when electrons can be moved in more than one direction, move them to the more electronegative atom. Drawing Resonance Forms There are several things that should be checked before and after drawing the resonance forms. The difference between the two structures is the location of double bond.

I consider, that you are mistaken. Let's discuss. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.
Idea good, it agree with you.