Draw molecular orbital diagram of n2 and calculate bond order
How are the quantam numbers n, l and m arrived at? Explain the significance of these quantam numbers. Write the postulates of Bohr's model of hydrogen atom. What are the limitations of Bohr's model of an atom?
None of the approaches we have described so far can adequately explain why some compounds are colored and others are not, why some substances with unpaired electrons are stable, and why others are effective semiconductors. These approaches also cannot describe the nature of resonance. Such limitations led to the development of a new approach to bonding in which electrons are not viewed as being localized between the nuclei of bonded atoms but are instead delocalized throughout the entire molecule. Just as with the valence bond theory, the approach we are about to discuss is based on a quantum mechanical model. Previously, we described the electrons in isolated atoms as having certain spatial distributions, called orbitals , each with a particular orbital energy.
Draw molecular orbital diagram of n2 and calculate bond order
Formation of Nitrogen molecule by Molecular Orbital Theory:. On calculating bond order we ignore the combination of inner shells i. KK' as they have two electrons in both bonding and anti bonding orbitals. Nitrogen molecule has 3 bonds. Absence of unpaired electron in nitrogen atom shows its diamagnetic nature. Byju's Answer. Explain the formation of nitrogen molecule by molecular orbital theory MOT. Open in App. Molecular Orbital Theory Molecular orbital theory, describes the formation of molecules, by the overlap of two atomic orbitals. The molecular orbitals are divided into bonding, antibonding and non bonding.
Furthermore, because the computed molecular orbitals extend over the entire molecule, they are often difficult to represent in a way that is easy to visualize. A molecule must have as many molecular orbitals as there are atomic orbitals. Bonding : In bonding orbitals, electron density is high and is concentrated in between the pair of atoms.
Draw the molecular orbital diagram of N 2 and calculate the bond order. Molecular orbital diagram of N 2. Hence, bond order of N 2 is 3. Also calculate their bond order? Byju's Answer. Open in App. Molecular orbital diagram: The molecular orbital diagram describes the chemical bonding in a molecule based on molecular orbital theory MOT and linear combination of atomic orbital LCAO.
Understanding the bond order of a molecule is a crucial step in analyzing its chemical properties and reactivity. The bond order, derived from a molecular orbital diagram, provides insights into the strength, stability, and nature of chemical bonds within a molecule. What are Molecular Orbitals — Definition, Features 2. Molecular orbitals are regions of space where electrons are likely to be found in a molecule. They are formed by the overlapping of atomic orbitals , which are regions of space where electrons are localized around individual atoms. Molecular orbitals result from the linear combination of atomic orbitals, where atomic orbitals from different atoms overlap and create bonding and antibonding orbitals. Bonding orbitals are lower in energy and stabilize the molecule, while antibonding orbitals are higher in energy and destabilize the molecule.
Draw molecular orbital diagram of n2 and calculate bond order
The molecular orbital MO theory is a powerful and extensive approach which describes electrons as delocalized moieties over adjacent atoms. The MO theory incorporates the wave character of electrons in developing MO diagrams. MO diagrams predict physical and chemical properties of a molecule such as shape, bond energy, bond length and bond angle. The objective of this wiki is to provide readers with the fundamental steps in constructing simple homonuclear and heteronuclear diatomic molecular orbital diagrams. These steps may then be extrapolated to construct more difficult polyatomic diagrams. Molecular Orbitals The region an electron is most likely to be found in a molecule. A MO is defined as the combination of atomic orbitals.
Halal places near me
Hence the molecular orbital theory of bonding is a delocalized approach. Asked for: molecular orbital energy-level diagram, valence electron configuration, bond order, and stability. A molecular orbital that forms when atomic orbitals or orbital lobes with the same sign interact to give increased electron probability between the nuclei due to constructive reinforcement of the wave functions. Each fluorine has 7 valence electrons, so there are a total of 14 valence electrons in the F 2 molecule. The only way to explain this behavior was for O 2 to have unpaired electrons, making it paramagnetic, exactly as predicted by molecular orbital theory. Calculate the bond order and discuss the extra stability and diamagnetic nature of the molecule. If they were not so slow, all organic substances, including this book and you, would disappear in a puff of smoke! The other electrons on Cl are best viewed as nonbonding. Consequently, reactions of this type are usually exceedingly slow. Molecular orbital diagram of N 2. Calculate the bond order of Recall that the probability density is proportional to the square of the wave function. A Because sodium has a [Ne]3 s 1 electron configuration, the molecular orbital energy-level diagram is qualitatively identical to the diagram for the interaction of two 1 s atomic orbitals. None of the approaches we have described so far can adequately explain why some compounds are colored and others are not, why some substances with unpaired electrons are stable, and why others are effective semiconductors. KK' as they have two electrons in both bonding and anti bonding orbitals.
Draw the molecular orbital diagram of N 2 and calculate the bond order.
Molecular Orbitals for Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules Diatomic molecules with two different atoms are called heteronuclear diatomic molecules. Write the magnetic nature of N 2 and O 2 molecules. The molecular orbital approach correctly predicts that the O 2 molecule has two unpaired electrons and hence is attracted into a magnetic field. Given: chemical species Asked for: molecular orbital energy-level diagram, bond order, and number of unpaired electrons Strategy: Write the valence electron configuration of sulfur and determine the type of molecular orbitals formed in S 2. Thus F 2 is predicted to have a stable F—F single bond, in agreement with experimental data. As discussed previously , electrons can behave like waves. In the solid state, however, all the alkali metals and the alkaline earth metals exist as extended lattices held together by metallic bonding. The electron configuration of a molecule is shown by placing the correct number of electrons in the appropriate energy-level diagram, starting with the lowest-energy orbital and obeying the Pauli principle; that is, placing only two electrons with opposite spin in each orbital. The bonding in any diatomic molecule with two He atoms can be described using the following molecular orbital diagram:. Thus molecular orbital theory and the Lewis electron-pair approach agree that a single bond containing two electrons has a bond order of 1.

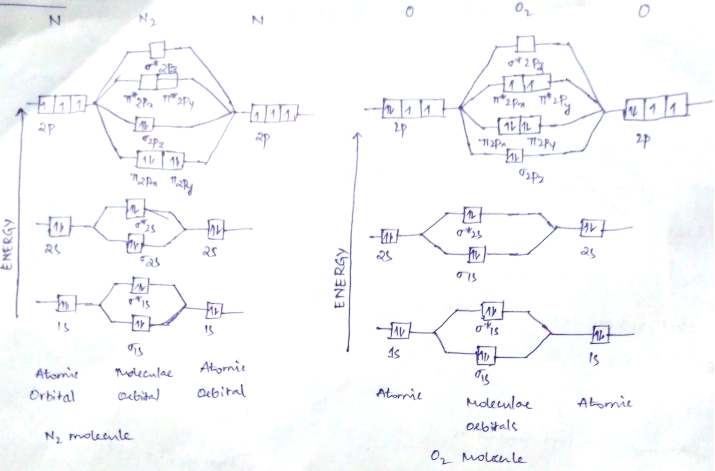
0 thoughts on “Draw molecular orbital diagram of n2 and calculate bond order”