Conserved domain database
Identify the putative function of a protein sequence.
Conserved Domains and Protein Classification. HOW TO. Citing the Resources. The conserved domain database in Nucleic Acids Res. CD-Search: protein domain annotations on the fly. Epub Nov
Conserved domain database
Toggle navigation. Repository details Conserved Domain database. General Institutions Terms Standards Name of repository. Additional name s. Repository URL. Subject s. The Conserved Domain Database is a resource for the annotation of functional units in proteins. Content type s. Structured graphics Scientific and statistical data formats Images other. Keyword s. Persistent identifier s of the repository. Repository size.
CD-Search: protein domain annotations on the fly. Shennan Lu.
CDD has been available publicly for over 20 years and has grown substantially during that time. Maintaining an archive of pre-computed annotation continues to be a challenge and has slowed down the cadence of CDD releases. CDD aims to collect a comprehensive set of protein and domain family models, and it does allow for considerable redundancy in the model set, to ensure good coverage of the protein space. Models that provide significantly overlapping annotation are clustered into protein domain superfamilies, and when domain annotation fails to exceed critical model-specific score thresholds, CDD by default reports superfamily annotation rather than individual model hits. For each model, we compute a consensus sequence, which is used for display purposes only, and reflects the length of the position-specific score matrix PSSM.
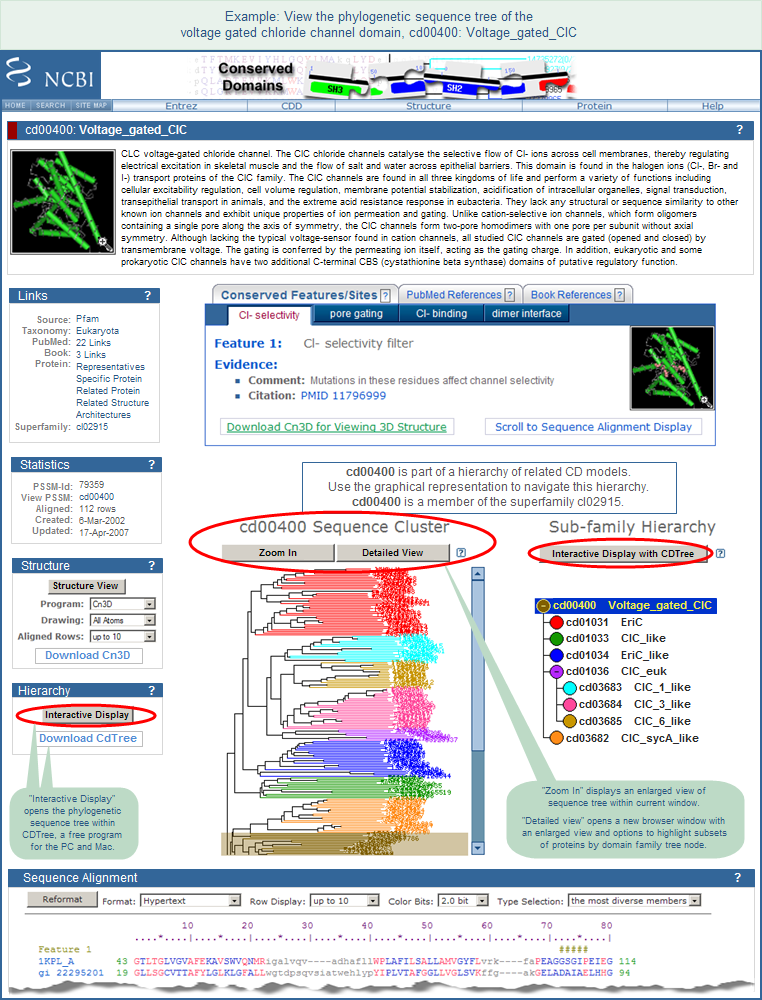
Identify the putative function of a protein sequence. Identify a protein's classification based on domain architecture. Identify the amino acids in a protein sequence that are putatively involved in functions such as binding or catalysis, as mapped from conserved domain annotations to the query sequence. View a query protein sequence embedded within the multiple sequence alignment of a domain model. Interactively view the 3D structure of a conserved domain. Find other proteins with similar domain architecture. Interactively view the phylogenetic sequence tree for a conserved domain model of interest with or without a query sequence embedded. Conserved Domains and Protein Classification. HOW TO. CDD is a protein annotation resource that consists of a collection of well-annotated multiple sequence alignment models for ancient domains and full-length proteins.
Conserved domain database
The Conserved Domain Database CDD is a database of well-annotated multiple sequence alignment models and derived database search models, for ancient domains and full-length proteins. These two classifications coincide rather often, as a matter of fact, and what is found as an independently folding unit of a polypeptide chain also carries specific function. Domains are often identified as recurring sequence or structure units, which may exist in various contexts. In molecular evolution such domains may have been utilized as building blocks, and may have been recombined in different arrangements to modulate protein function. CDD defines conserved domains as recurring units in molecular evolution, the extents of which can be determined by sequence and structure analysis. Manually curated models are organized hierarchically if they describe domain families that are clearly related by common descent.
Dan murphys specials
Table 2. Please consider expanding the lead to provide an accessible overview of all important aspects of the article. Oxford Academic. Marc Gwadz. The results of CD-Search are presented as an annotation of protein domains on the user query sequence illustrated example , and can be visualized as domain multiple sequence alignments with embedded user queries. Advanced Search. Journal Article. Relying on domain profiles allows CDART to be fast and, because it relies on annotated functional domains, informative. CDD: a database of conserved domain alignments with links to domain three-dimensional structure. Maintaining an archive of pre-computed annotation continues to be a challenge and has slowed down the cadence of CDD releases. Improving the consistency of domain annotation within the Conserved Domain Database. James S.
Protein or Nucleotide Query Sequence. Batch of Protein Sequences. Find proteins with similar domain architectures.
Revised 1 December Zhouxi Wang. Curated collections of representative sequences offer a viable alternative, and so do profile database searches, as collections of profile models that represent evolutionarily conserved sequence fragments or domains are not expected to grow at an exorbitant pace. It enables you to view a graphical display of the concise or full search result for any individual protein from your input list, or to download the results for the complete set of proteins. The results of CD-Search are presented as an annotation of protein domains on the user query sequence illustrated example , and can be visualized as domain multiple sequence alignments with embedded user queries. Enhanced Publication. Typically, they will be assigned more generic names, while specific domain architectures may group more closely releated proteins and be assigned more precise and informative names and functional descriptions. Tatusov R. CDD: a database of conserved domain alignments with links to domain three-dimensional structure. Advanced Search. Hurwitz, Christopher J. Conserved Domains and Protein Classification. James S. In early , CDD version v3.

0 thoughts on “Conserved domain database”