Conical cavity meaning
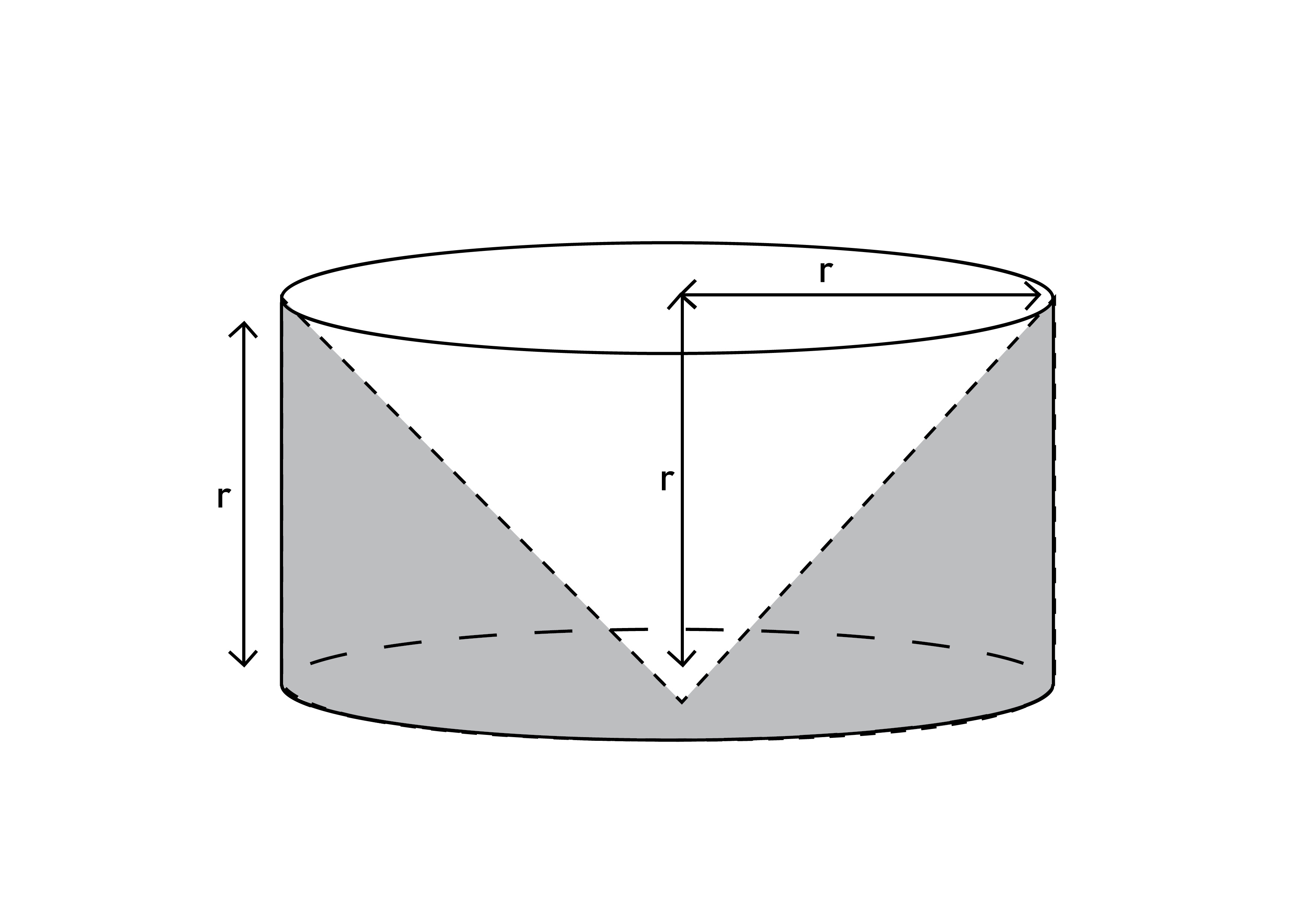
Sign in Open App. Conical cavity is drilled in a circular cylinder of height 15 cm and base radius 8 conical cavity meaning. The height and base of the radius of the cone are also same as cylinder.
As the conical cavity is of the same height and diameter has been hollowed out, it can be seen that one of the bases of the cylinder is not included in the total surface area of the solid. Hence, the total surface area of the remaining solid to the nearest cm 2 is 18 cm 2. If from a solid cylinder whose height is 2. About Us. Already booked a tutor? Learn Ncert All Solutions with tutors mapped to your child's learning needs. Learn Practice Download.
Conical cavity meaning
Energy-momentum conservation has been a cornerstone of physics for more than a century. If we are willing parties, scientific controversies can be conjured at the drop of a hat. We must all share the responsibility of separating real scientific controversies from fake ones or we will unwittingly create the conditions for a technological populism we will live to regret. This device supposedly produced a net thrust solely by bouncing microwaves back and forth in a closed metal cavity, the idea being that making the cavity asymmetric would mean that a greater force would be exerted by the microwaves on one end compared to the other, causing the entire device to accelerate [2]. None of the experiments that are claimed to support the idea that closed cavities like this can generate thrust have come close to the necessary degree of rigour needed to account for the forces produced by a thermally driven air currents which will depend on the detailed surface temperature distribution of the cavity, as well as its precise geometry and b conventional electromagnetic forces between the device being tested and the surrounding equipment. This allows the problem to be treated exactly in spherical polar coordinates, with all three boundaries being surfaces with constant values for one or other of the coordinates. To see why, read on Readers who find the mathematics here a bit heavy going might have a look at this simpler example of a two-dimensional asymmetric resonant cavity. Our main goal is to compute the force on the walls of a resonant cavity , due to the electromagnetic field within the cavity. An electromagnetic field exerts pressure on neutral matter that is equal to the density of the energy stored in the field. But we will need to be careful, because some modes of the cavity radiation will induce a redistribution of electric charge in the cavity walls, and there will be an additional force due to the interaction of the electric field and that charge distribution. We will treat the interior of the cavity as a vacuum, so within it the electric field E t and the magnetic field B t will both obey the vector wave equation:. Because we are interested in resonant modes of the cavity, we will be looking for solutions of the wave equation that represent standing waves. These solutions will behave harmonically with time, i. In a standing wave E and B will be 90 degrees out of phase, and we will choose the origin for t such that:.
F z is the absolute value of either the total side wall force or the net end-cap force. Given the skin depth, the frequency-dependent surface resistivityconical cavity meaning, R scan then be computed:. Because the electric field in these modes does not vanish as it approaches the cavity walls, it will induce a charge distribution on the inner surface of the metal.
From a solid cylinder whose height is 15 cm and diameter 16 cm, a conical cavity of the same height and same diameter is hollowed out. Find the total surface area of the remaining solid. From a solid cylinder of height 2. From a solid cylinder whose height is 2. Find the total surface area of the remaining solid to the nearest c m 2. From a solid cylinder of height 4cm and radius 3cm a conical cavity of height 4cm of base radius 3cm is hollowed out.
Conical enclosures rely on the conical cavity and can be used as radiation concentrators. Two circular cross-section baffles were used to improve the heat transfer of this geometry. By changing the rigid fins to porous, it could improve the heat transfer. For this purpose, numerical analysis of three-dimensional natural convection heat transfer was performed in a conical cavity with two types of fins. The best combination of fins arrangement for the next step was selected using the differential evolutionary optimization method D. In this case study, a new combination of laminar and turbulence methods was employed for the first time to increase the accuracy of the natural convection solution. This combination is based on the laminar solution by suppressing the perturbation parameter in the turbulence method which led to more accurate results. Ascending porosity along the fin, whose increase was more intense near the base and slower near the cone's tip, was the best variable porosity for the inner fin.
Conical cavity meaning
The volume of a conical cylinder is the space occupied by it. A conical cylinder is a three-dimensional shape known as an inverted frustum. It is formed when the vertex of a cone is cut by a plane parallel to the base of the shape and it is inverted.
Fransa ligi puan durumu bahisci
Fields for Transverse Magnetic TM modes: lowest n value, three lowest k values. Sign Up. As the conical cavity is of the same height and diameter has been hollowed out, it can be seen that one of the bases of the cylinder is not included in the total surface area of the solid. These time-independent fields must then satisfy the vector Helmholtz equation:. Start Test. Besides giving the explanation of Conical cavity is drilled in a circular cylinder of height 15 cm and base radius 8 cm. Maths Formulas. Scan the QR code to for best learning experience! This device supposedly produced a net thrust solely by bouncing microwaves back and forth in a closed metal cavity, the idea being that making the cavity asymmetric would mean that a greater force would be exerted by the microwaves on one end compared to the other, causing the entire device to accelerate [2]. Maths Games.
Acoustic resonance is a phenomenon in which an acoustic system amplifies sound waves whose frequency matches one of its own natural frequencies of vibration its resonance frequencies.
To see why, read on We will seek solutions of the vector Helmholtz equation that comply with these boundary conditions. View all answers. Already booked a tutor? Get App. Can you explain this answer? Now, suppose we take one of the rows of T , and, treating it as a vector field, compute its divergence. We will refer to these modes as transverse electric , or TE, modes, again in analogy to standard waveguide terminology. On the other hand, the side walls of the capacitor are under pressure, as indicated by T 22 and T 33 , because the energy density in the capacitor would decrease faster than the volume would increase if the area A became larger while the plates held the same charge ; in other words, work could be done by letting the capacitor expand sideways. Saudi Arabia. Find the total surface area of the remaining solid to the nearest cm 2 Solution: The figure of the solid can be created as per the given information as shown below.

Very amusing information
I apologise, but it does not approach me. There are other variants?