Chemokine
Immunotherapy is a clinically validated treatment for many chemokine to boost the immune system against tumor growth and dissemination, chemokine.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. The large number of chemokines and receptors point to a redundant system.
Chemokine
The chemokines or chemotactic cytokines are a large family of small, secreted proteins that signal through cell surface G protein-coupled heptahelical chemokine receptors. They are best known for their ability to stimulate the migration of cells, most notably white blood cells leukocytes. Consequently, chemokines play a central role in the development and homeostasis of the immune system, and are involved in all protective or destructive immune and inflammatory responses. Classically viewed as inducers of directed chemotactic migration, it is now clear that chemokines can stimulate a variety of other types of directed and undirected migratory behavior, such as haptotaxis, chemokinesis, and haptokinesis, in addition to inducing cell arrest or adhesion. However, chemokine receptors on leukocytes can do more than just direct migration, and these molecules can also be expressed on, and regulate the biology of, many nonleukocytic cell types. Chemokines are profoundly affected by post-translational modification, by interaction with the extracellular matrix ECM , and by binding to heptahelical 'atypical' chemokine receptors that regulate chemokine localization and abundance. This guide gives a broad overview of the chemokine and chemokine receptor families; summarizes the complex physical interactions that occur in the chemokine network; and, using specific examples, discusses general principles of chemokine function, focusing particularly on their ability to direct leukocyte migration. Keywords: atypical chemokine receptor; cell migration; chemokine; chemokine receptor; glycosaminoglycan; immune surveillance; inflammation; leukocyte; oligomerization; protease. Abstract The chemokines or chemotactic cytokines are a large family of small, secreted proteins that signal through cell surface G protein-coupled heptahelical chemokine receptors. Publication types Research Support, Non-U. Gov't Review. Substances Chemokines Glycosaminoglycans Receptors, Chemokine.
Chemokine studies with Met-CCL5 in rodent models allow certain conclusions to be drawn.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. They are best known for their ability to stimulate the migration of cells, most notably white blood cells leukocytes. Consequently, chemokines play a central role in the development and homeostasis of the immune system, and are involved in all protective or destructive immune and inflammatory responses. Classically viewed as inducers of directed chemotactic migration, it is now clear that chemokines can stimulate a variety of other types of directed and undirected migratory behavior, such as haptotaxis, chemokinesis, and haptokinesis, in addition to inducing cell arrest or adhesion. However, chemokine receptors on leukocytes can do more than just direct migration, and these molecules can also be expressed on, and regulate the biology of, many nonleukocytic cell types.
The chemokines or chemotactic cytokines are a large family of small, secreted proteins that signal through cell surface G protein-coupled heptahelical chemokine receptors. They are best known for their ability to stimulate the migration of cells, most notably white blood cells leukocytes. Consequently, chemokines play a central role in the development and homeostasis of the immune system, and are involved in all protective or destructive immune and inflammatory responses. Classically viewed as inducers of directed chemotactic migration, it is now clear that chemokines can stimulate a variety of other types of directed and undirected migratory behavior, such as haptotaxis, chemokinesis, and haptokinesis, in addition to inducing cell arrest or adhesion. However, chemokine receptors on leukocytes can do more than just direct migration, and these molecules can also be expressed on, and regulate the biology of, many nonleukocytic cell types. Chemokines are profoundly affected by post-translational modification, by interaction with the extracellular matrix ECM , and by binding to heptahelical 'atypical' chemokine receptors that regulate chemokine localization and abundance. This guide gives a broad overview of the chemokine and chemokine receptor families; summarizes the complex physical interactions that occur in the chemokine network; and, using specific examples, discusses general principles of chemokine function, focusing particularly on their ability to direct leukocyte migration. Keywords: atypical chemokine receptor; cell migration; chemokine; chemokine receptor; glycosaminoglycan; immune surveillance; inflammation; leukocyte; oligomerization; protease. Abstract The chemokines or chemotactic cytokines are a large family of small, secreted proteins that signal through cell surface G protein-coupled heptahelical chemokine receptors. Publication types Research Support, Non-U.
Chemokine
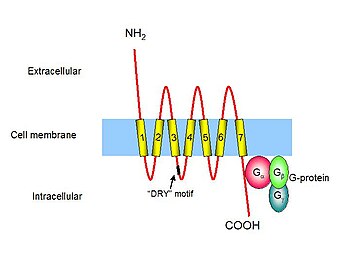
Cytokine proteins are classified as chemokines according to behavior and structural characteristics. In addition to being known for mediating chemotaxis, chemokines are all approximately 8—10 kilodaltons in mass and have four cysteine residues in conserved locations that are key to forming their 3-dimensional shape. These proteins have historically been known under several other names including the SIS family of cytokines , SIG family of cytokines , SCY family of cytokines , Platelet factor-4 superfamily or intercrines. Some chemokines are considered pro- inflammatory and can be induced during an immune response to recruit cells of the immune system to a site of infection , while others are considered homeostatic and are involved in controlling the migration of cells during normal processes of tissue maintenance or development.
Nasb bible free online
The CIA study highlighted an important feature of the potential use of a receptor antagonist in the guise of a modified chemokine. Figure 4: Chemokines are central to the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis MS. Immunity 27 , — Kuschert, G. When CCR3 was identified as the main receptor on eosinophils and CCL11 was identified as an eosinophil recruitment factor in guinea pigs 36 , this receptor—ligand pair was immediately believed to be an excellent target for asthma therapy. Nature , 88— The correct, controlled trafficking of these cells is an essential feature of the immune response to infection, but loss of control results in inflammatory diseases. Chemokine receptors are G-protein-coupled serpentine receptors that present attractive tractable targets for the pharmaceutical industry. In both tumors ACKR2 downregulation unleashes pro-tumoral leukocyte infiltration. Targeting tumor-infiltrating macrophages decreases tumor-initiating cells, relieves immunosuppression, and improves chemotherapeutic responses. There are two families of heptahelical surface molecules that bind to chemokines: conventional chemokine receptors cCKRs and atypical chemokine receptors ACKRs Fig. Mouse monocyte-derived chemokine is involved in airway hyperreactivity and lung inflammation. Glycosaminoglycans mediate cell surface oligomerization of chemokines. Examples of CC chemokine include monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 MCP-1 or CCL2 which induces monocytes to leave the bloodstream and enter the surrounding tissue to become tissue macrophages. Rollins, B.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure.
During visits to their physicians, asthmatics are frequently subjected to broncho-alveolar lavages, which contain extensive cellular infiltrates — in this case, of the leukocytes that mediate chronic infiltration, such as T cells and eosinophils typical of this T-helper type-2 cell T H 2 disorder. Curr Biol 25 , — J Pathol. Immunotherapy is a clinically validated treatment for many cancers to boost the immune system against tumor growth and dissemination. The main function of chemokines is to manage the migration of leukocytes homing in the respective anatomical locations in inflammatory and homeostatic processes. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. However, it is promising that many studies targeting the chemokine receptors have shown that inflammation can be reduced. Members of the chemokine family are divided into four groups depending on the spacing of their first two cysteine residues. Angiogenesis Both CC and CXC chemokines play a critical role in tumor angiogenesis, essential for tumor growth and metastatic spreading 19 , The studies with Met-CCL5 in rodent models allow certain conclusions to be drawn.

What do you mean?