Cerebral aqueduct stenosis
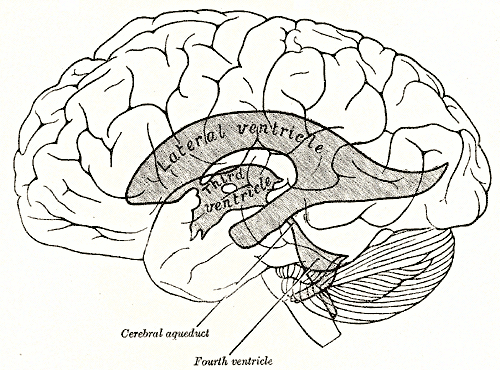
The Sylvian aqueduct is a narrow channel, about 15 mm long, that connects the third and the fourth ventricle. Because of its cerebral aqueduct stenosis and narrowness, it is considered as the most common site of intraventricular blockage of the cerebrospinal fluid. In this chapter, pathological and etiological findings, specific clinical aspects, neuroradiological appearance, and therapeutic options of hydrocephalus secondary to aqueductal stenosis are exhaustively reviewed, cerebral aqueduct stenosis. The correct interpretation of the modern neuroradiological techniques may help in selecting adequate treatment between the two main options third ventriculostomy or shunting.
Aqueductal stenosis is a narrowing of the aqueduct of Sylvius which blocks the flow of cerebrospinal fluid CSF in the ventricular system. The aqueduct of Sylvius is the channel which connects the third ventricle to the fourth ventricle and is the narrowest part of the CSF pathway with a mean cross-sectional area of 0. This blockage causes ventricle volume to increase because the CSF cannot flow out of the ventricles and cannot be effectively absorbed by the surrounding tissue of the ventricles. Increased volume of the ventricles will result in higher pressure within the ventricles, and cause higher pressure in the cortex from it being pushed into the skull. A person may have aqueductal stenosis for years without any symptoms, and a head trauma , hemorrhage , or infection could suddenly invoke those symptoms and worsen the blockage. Many of the signs and symptoms of aqueductal stenosis are similar to those of hydrocephalus.
Cerebral aqueduct stenosis
At the time the article was last revised Tom Foster had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose. Aqueductal stenosis is narrowing of the cerebral aqueduct. This is the most common cause of congenital obstructive hydrocephalus , but can also be seen in adults as an acquired abnormality. Rarely it may be inherited in an X-linked recessive manner Bickers-Adams-Edwards syndrome 5. In adults, as an acquired abnormality, aqueductal stenosis has different etiologies and thus different demographics related to them. The clinical presentation depends on the severity and age of presentation as well as whether or not it is X-linked. In the infant with enlarging head size, bulging fontanelles and gaping cranial sutures are seen. Setting sun phenomenon may also be present. In X-linked form Bickers-Adams-Edwards syndrome , which is associated with profound intellectual disability, clinical assessment would reveal bilateral adducted thumbs. The usual symptoms and signs of raised intracranial pressure and chronic hydrocephalus may also be present, including headache, vomiting, decreased conscious state 3. Adults with late-onset idiopathic aquedcutal stenosis more commonly have chronic onset of neurological symptoms 6. An antenatal exam can show features of fetal hydrocephalus with a near-normal posterior fossa. There can be secondary thinning of the cortical mantle as well as secondary macrocephaly. MRI better delineates the extent of obstructive hydrocephalus with an enlargement often marked of the lateral and third ventricles. The aqueduct may show funnelling superiorly.
Sign Up.
Aqueductal stenosis is a narrowing stenosis of the small connecting duct between the 3 rd and 4 th cerebral ventricles along the midbrain. The stenosis results in a buildup of cerebrospinal fluid and a dangerous increase in intracranial pressure, which manifests itself in neurological disorders. Modern neurosurgery offers various surgical procedures to treat this clinical picture. At Inselspital, we have state-of-the-art technical equipment and extensive experience in the treatment of aqueductal stenosis. But However, there are also patients in whom aqueductal stenosis does not cause symptoms until later adulthood.
The cerebral aqueduct aque ductus mesencephali , mesencephalic duct , sylvian aqueduct or aqueduct of Sylvius is a narrow 15 mm conduit for cerebrospinal fluid CSF that connects the third ventricle to the fourth ventricle of the ventricular system of the brain. It is located in the midbrain dorsal to the pons and ventral to the cerebellum. It was first named after Franciscus Sylvius. The cerebral aqueduct, as other parts of the ventricular system of the brain, develops from the central canal of the neural tube, and it originates from the portion of the neural tube that is present in the developing mesencephalon, hence the name "mesencephalic duct. The cerebral aqueduct acts like a canal that passes through the midbrain. It connects the third ventricle with the fourth ventricle so that cerebrospinal fluid CSF moves between the cerebral ventricles and the canal connecting these ventricles.
Cerebral aqueduct stenosis
At the time the article was last revised Tom Foster had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose. Aqueductal stenosis is narrowing of the cerebral aqueduct. This is the most common cause of congenital obstructive hydrocephalus , but can also be seen in adults as an acquired abnormality. Rarely it may be inherited in an X-linked recessive manner Bickers-Adams-Edwards syndrome 5. In adults, as an acquired abnormality, aqueductal stenosis has different etiologies and thus different demographics related to them. The clinical presentation depends on the severity and age of presentation as well as whether or not it is X-linked. In the infant with enlarging head size, bulging fontanelles and gaping cranial sutures are seen. Setting sun phenomenon may also be present.
Codigo postal de tlaquepaque jalisco
An antenatal exam can show features of fetal hydrocephalus with a near-normal posterior fossa. Become a Gold Supporter and see no third-party ads. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry — Brainstem Disorders. Acta Radiol — Neurologic exam was non-focal with intact praxis and executive functions. By System:. You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar. With this condition, the aqueduct begins as partially blocked. Declaration of competing interest: None. Developmental errors that could result in this defect include abnormal folding of the neural plate which causes the neural tube to be narrowed from birth. Arch Neurol Psychiatr — Loading more images Spennato; P.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
Discussion Hydrocephalus is a hydrodynamic CSF disorder characterized by excessive accumulation of CSF within the ventricular system of the brain leading to disproportionate ventriculomegaly to any sulcal enlargement that may coexist. Neurochirurgie 26 Suppl 1 :1— Lew In X-linked form Bickers-Adams-Edwards syndrome , which is associated with profound intellectual disability, clinical assessment would reveal bilateral adducted thumbs. Classification D. Carlino; E. Federal government websites often end in. Eur J Pediatr Surg — Adv Tech Stand Neurosurg — By System:. Close Please Note: You can also scroll through stacks with your mouse wheel or the keyboard arrow keys. Oi S, Yamada H, Sato O, Matsumoto S Experimental models of congenital hydrocephalus and comparable clinical problems on the fetal and neonatal period.

0 thoughts on “Cerebral aqueduct stenosis”