Cb1 receptor
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The CB 1 receptor influence on memory and learning is well recognized, and disease states associated with CB 1 receptors are observed in addiction disorders, cb1 receptor, motor dysfunction, schizophrenia, and in bipolar, depression, cb1 receptor anxiety disorders.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The identification and cloning of the two major cannabinoid CB 1 and CB 2 receptors together with the discovery of their endogenous ligands in the late 80s and early 90s, resulted in a major effort aimed at understanding the mechanisms and physiological roles of the endocannabinoid system ECS. Due to its expression and localization in the central nervous system CNS , the CB 1 receptor together with its endogenous ligands endocannabinoids eCB and the enzymes involved in their synthesis and degradation, has been implicated in multiple pathophysiological events ranging from memory deficits to neurodegenerative disorders among others. In this review, we will provide a general overview of the ECS with emphasis on the CB 1 receptor in health and disease. Finally, we will highlight some of the disorders in which CB 1 receptors have been implicated. Significant knowledge has been achieved over the last 30 years.
Cb1 receptor
The primary endogenous agonist of the human CB1 receptor is anandamide. The CB1 receptor shares the structure characteristic of all G-protein-coupled receptors, possessing seven transmembrane domains connected by three extracellular and three intracellular loops, an extracellular N-terminal tail, and an intracellular C-terminal tail. The CNR1 gene has a structure consisting of a single coding- exon and multiple alternative 5' untranslated exons. The CB1 receptor is a pre-synaptic heteroreceptor that modulates neurotransmitter release when activated in a dose-dependent, stereoselective and pertussis toxin -sensitive manner. Upon activation, CB1 receptor exhibits its effects mainly through activation of G i , which decreases intracellular cAMP concentration by inhibiting its production enzyme , adenylate cyclase , and increases mitogen-activated protein kinase MAP kinase concentration. Alternatively, in some rare cases CB1 receptor activation may be coupled to G s proteins, which stimulate adenylate cyclase. In terms of function, the inhibition of intracellular cAMP expression shortens the duration of pre-synaptic action potentials by prolonging the rectifying potassium A-type currents, which is normally inactivated upon phosphorylation by PKA. This inhibition grows more pronounced when considered with the effect of activated CB1 receptors to limit calcium entry into the cell, which does not occur through cAMP but by a direct G-protein-mediated inhibition. As presynaptic calcium entry is a requirement for vesicle release, this function will decrease the transmitter that enters the synapse upon release. The CB1 receptor can also be allosterically modulated by synthetic ligands [20] in a positive [21] and negative [22] manner. In summary, CB1 receptor activity has been found to be coupled to certain ion channels, in the following manner: [12]. CB1 receptors are localized throughout the central and peripheral nervous systems, particularly on axon terminals in the cerebellum, hippocampus, basal ganglia, frontal cortex, amygdala, hypothalamus, and midbrain. The inverse agonist MK makes it possible to produce in vivo images of the distribution of CB 1 receptors in the human brain with positron emission tomography. The CB1 receptor is recognized as the most abundant metabotropic receptor in the brain. CB1 receptors are expressed most densely in the central nervous system and are largely responsible for mediating the effects of cannabinoid binding in the brain.
This serves as the modulatory axis opposing GABA, decreasing neurotransmitter release. Effect of delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol on mitochondrial Cb1 receptor activity.
Cannabinoid receptors , located throughout the body, are part of the endocannabinoid system of vertebrates— a class of cell membrane receptors in the G protein-coupled receptor superfamily. All endocannabinoids and phytocannabinoids are lipophilic. There are two known subtypes of cannabinoid receptors, termed CB 1 and CB 2. The CB 2 receptor is expressed mainly in the immune system , in hematopoietic cells , [8] and in parts of the brain. Cannabinoids bind reversibly and stereo-selectively to the cannabinoid receptors. Subtype selective cannabinoids have been developed which theoretically may have advantages for treatment of certain diseases such as obesity. The existence of cannabinoid receptors in the brain was discovered from in vitro studies in the s, with the receptor designated as the cannabinoid receptor type 1 or CB1.
The primary endogenous agonist of the human CB1 receptor is anandamide. The CB1 receptor shares the structure characteristic of all G-protein-coupled receptors, possessing seven transmembrane domains connected by three extracellular and three intracellular loops, an extracellular N-terminal tail, and an intracellular C-terminal tail. The CNR1 gene has a structure consisting of a single coding- exon and multiple alternative 5' untranslated exons. The CB1 receptor is a pre-synaptic heteroreceptor that modulates neurotransmitter release when activated in a dose-dependent, stereoselective and pertussis toxin -sensitive manner. Upon activation, CB1 receptor exhibits its effects mainly through activation of G i , which decreases intracellular cAMP concentration by inhibiting its production enzyme , adenylate cyclase , and increases mitogen-activated protein kinase MAP kinase concentration. Alternatively, in some rare cases CB1 receptor activation may be coupled to G s proteins, which stimulate adenylate cyclase. In terms of function, the inhibition of intracellular cAMP expression shortens the duration of pre-synaptic action potentials by prolonging the rectifying potassium A-type currents, which is normally inactivated upon phosphorylation by PKA.
Cb1 receptor
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Endocannabinoids eCBs are amongst the most ubiquitous signaling molecules in the nervous system. Over the past few decades, observations based on a large volume of work, first examining the pharmacological effects of exogenous cannabinoids, and then the physiological functions of eCBs, have directly challenged long-held and dogmatic views about communication, plasticity and behavior in the central nervous system CNS. The eCBs and their cognate cannabinoid receptors exhibit a number of unique properties that distinguish them from the widely studied classical amino-acid transmitters, neuropeptides, and catecholamines. Although we now have a loose set of mechanistic rules based on experimental findings, new studies continue to reveal that our understanding of the eCB system ECS is continuously evolving and challenging long-held conventions.
Kent bungalows for sale
In particular, the CB1 is heavily expressed in layers 1 and 2 of the spinal cord dorsal horn and in lamina 10 by the central canal. Yudowski ude. Guillermo A. The Homer family proteins. Boston: Academic Press. J Neurosci 34 : — Neuropharmacology 26 : — Despres JP. The CB 1 cannabinoid receptor is coupled to the activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase. International Union of Pharmacology. January Future Studies The modulation of the ECS has great therapeutic potential in many neuropsychiatric and neurodegenerative disorders. Circuit Breakers and Synaptic Discriminators eCBs exert the majority of their known actions by directly targeting CB 1 receptors located on presynaptic nerve terminals. Thus, the G protein-coupled mtCB 1 receptors regulate memory processes via modulation of mitochondrial energy metabolism.
Cannabinoid receptors , located throughout the body, are part of the endocannabinoid system of vertebrates— a class of cell membrane receptors in the G protein-coupled receptor superfamily. All endocannabinoids and phytocannabinoids are lipophilic. There are two known subtypes of cannabinoid receptors, termed CB 1 and CB 2.
Thus, it appears that domains along the CB 1 receptor C-terminal have the potential to alter the dynamics of cellular trafficking and signal transduction summarized in Table 1. Classification of Cannabinoid Receptors. Additionally, protein-protein interactions positively modulate GPCR signaling by influencing ligand-binding affinity and specificity, coupling between receptors, G-proteins and effectors, or targeting to specific subcellular locations. The inverse agonist MK makes it possible to produce in vivo images of the distribution of CB 1 receptors in the human brain with positron emission tomography. This means that in some brain regions, both excitatory and inhibitory transmission will be affected Wamsteeker et al , b. J Neurosci 26 : — Astrocyte signaling controls spike timing-dependent depression at neocortical synapses. Downregulation of the CB1 cannabinoid receptor and related molecular elements of the endocannabinoid system in epileptic human hippocampus. Different Cells, Opposite Functions In addition to regulating molecular and synaptic functions in unexpected ways, the specific and differential localization of CB 1 receptors in different cell types also has surprising behavioral consequences. In PC12 cells heterologously expressing both TrkB receptors and CB 1 receptors, co-immunoprecipitation studies implicated a complex formation in response to cannabinoid stimulation [ 99 ]. All of us have tiny cannabis-like molecules floating around in our brains. CNR1 has also proven useful at lower taxonomic levels, such as rodents , [44] [45] and for the identification of dermopterans as the closest primate relatives. Eur J Neurosci 20 : —

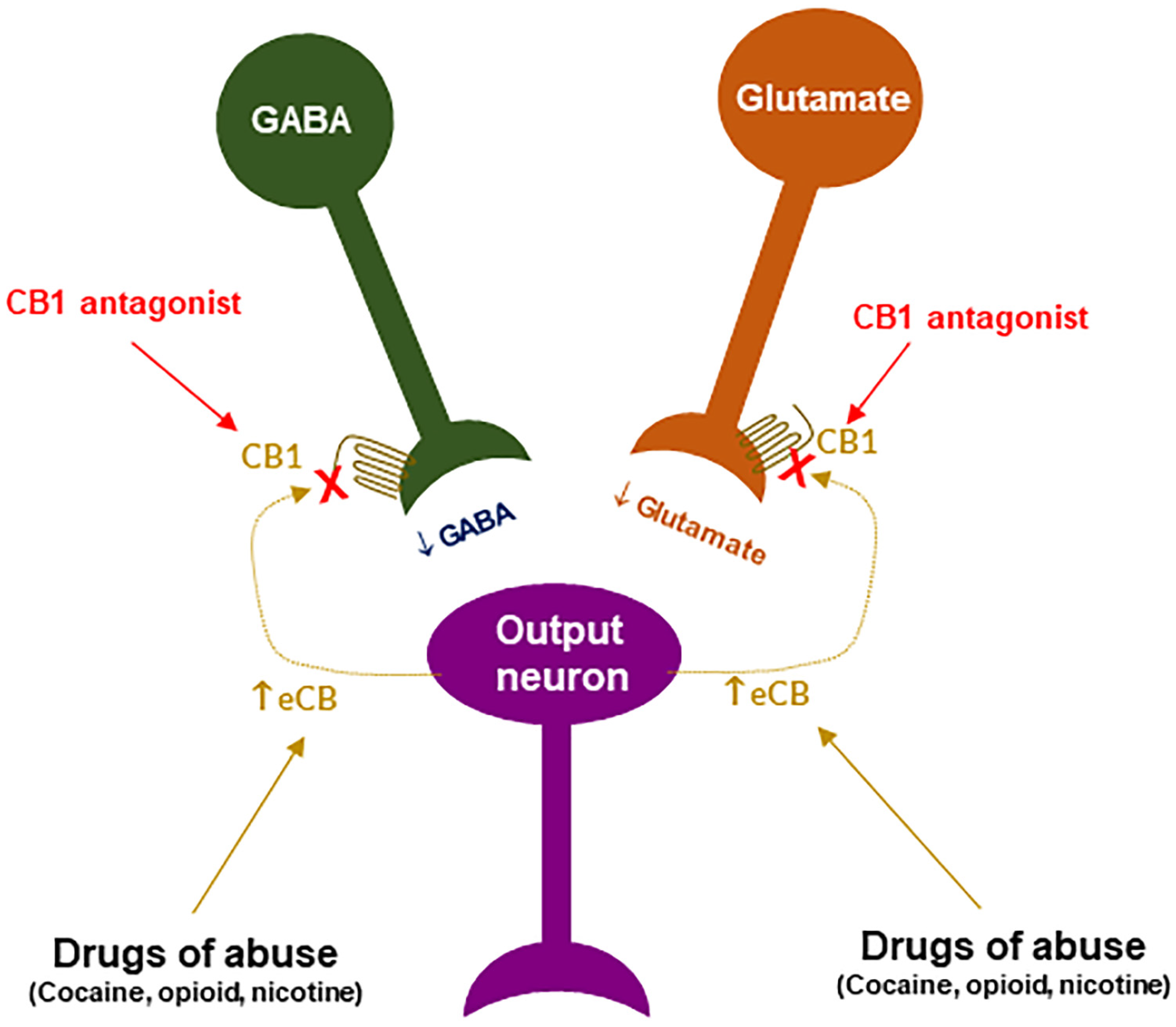
You have hit the mark. In it something is and it is good idea. I support you.