Caudate nucleus
The caudate nucleus is one of the structures that make up the corpus striatumwhich is a component of the basal ganglia in the human brain, caudate nucleus. The caudate is also one of the brain structures which compose caudate nucleus reward system and functions as part of the cortico — basal ganglia — thalamic loop.
Deep within each half of the brain lies the caudate nucleus. The caudate nucleus is a pair of brain structures that make up part of the basal ganglia. It helps control high-level functioning, including:. The basal ganglia are neuron cell bodies found deep within the brain involved with movement, behavior, and emotions. This brain circuit receives information from the cerebral cortex, which is a layer of grey matter in the outer brain linked to higher cognitive functions such as information processing and learning.
Caudate nucleus
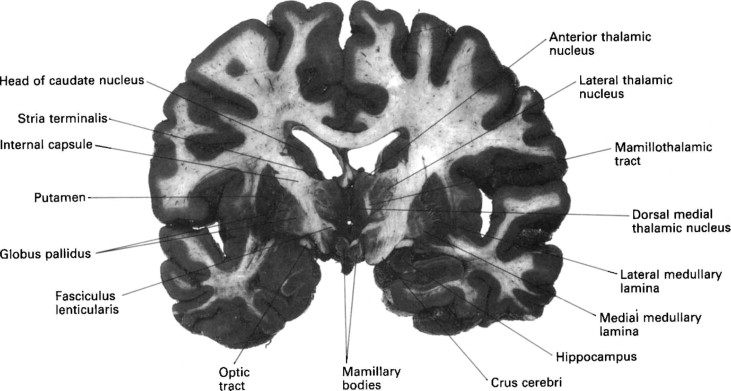
It plays a critical role in various higher neurological functions. Each caudate nucleus is composed of a large anterior head, a body, and a thin tail that wraps anteriorly such that the caudate nucleus head and tail can be visible in the same coronal cut. When combined with the putamen, the pair is referred to as the striatum and is often considered jointly in function. The striatum is the major input source for the basal ganglia, which also includes the globus pallidus, subthalamic nucleus, and substantia nigra. These deep brain structures together largely control voluntary skeletal movement. The caudate nucleus functions not only in planning the execution of movement, but also in learning, memory, reward, motivation, emotion, and romantic interaction. Input to the caudate nucleus travels from the cortex, mostly the ipsilateral frontal lobe. Efferent projections from the caudate nucleus travel to the hippocampus, globus pallidus, and thalamus. Research has implicated caudate nucleus dysfunction in several pathologies, including Huntington and Parkinson disease, various forms of dementia, ADHD, bipolar disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder, and schizophrenia. Publication types Study Guide.
ProQuest
At the time the article was last revised Yoshi Yu had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose. Caudate nuclei are paired nuclei which along with the globus pallidus and putamen are referred to as the corpus striatum , and collectively make up the basal ganglia. The caudate nuclei have both motor and behavioral functions, in particular maintaining body and limb posture, as well as controlling approach-attachment behaviors, respectively 3. The caudate nucleus is located lateral to the lateral ventricles, with the head lateral to the frontal horn, and body lateral to the body of the lateral ventricle. The tail of the caudate nucleus terminates immediately above the temporal horn of the ventricle. It is bound laterally by the anterior crus of the internal capsule. The head of the caudate nucleus is supplied by the recurrent artery of Heubner , a small branch from the A2 sometimes the A1 segment of the anterior cerebral artery.
Our decisions often balance what we observe and what we desire. A prime candidate for implementing this complex balancing act is the basal ganglia pathway, but its roles have not yet been examined experimentally in detail. Here, we show that a major input station of the basal ganglia, the caudate nucleus, plays a causal role in integrating uncertain visual evidence and reward context to guide adaptive decision-making. In monkeys making saccadic decisions based on motion cues and asymmetric reward-choice associations, single caudate neurons encoded both sources of information. These results imply that the caudate nucleus plays causal roles in coordinating decision processes that balance external evidence and internal preferences.
Caudate nucleus
At the time the article was last revised Yoshi Yu had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose. Caudate nuclei are paired nuclei which along with the globus pallidus and putamen are referred to as the corpus striatum , and collectively make up the basal ganglia. The caudate nuclei have both motor and behavioral functions, in particular maintaining body and limb posture, as well as controlling approach-attachment behaviors, respectively 3. The caudate nucleus is located lateral to the lateral ventricles, with the head lateral to the frontal horn, and body lateral to the body of the lateral ventricle. The tail of the caudate nucleus terminates immediately above the temporal horn of the ventricle. It is bound laterally by the anterior crus of the internal capsule. The head of the caudate nucleus is supplied by the recurrent artery of Heubner , a small branch from the A2 sometimes the A1 segment of the anterior cerebral artery. The superior aspect of the head and the body of the caudate are supplied by the lenticulostriate perforators from the middle cerebral artery.
Multi disc cd player
The American Journal of Psychiatry. Disclosure: Margaret Driscoll declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies. Imaging of gaps in digital joints by measurement of ultrasound transmission using a linear array. The vascular supply of the functional compartments of the human striatum. Authors Margaret E. A study of Parkinson's patients see below may also contribute to a growing body of evidence. In this vein, the two are functionally distinct not as a result of structural differences, but merely due to the topographical distribution of function. These deep brain structures together largely control voluntary skeletal movement. Lesions of the anterior caudate nucleus result in abnormal behavior, which does not correspond to rewards. Some brain specialists suspect variations in the caudate nucleus may play a role in the development of several neurological and psychiatric disorders.
Deep within each half of the brain lies the caudate nucleus. The caudate nucleus is a pair of brain structures that make up part of the basal ganglia.
The medial dorsal striatum is involved in goal-directed and flexible behavior. Through case studies of both exceptional people as well as those with disorders, Bizarre takes us on a fascinating journey in which we learn more about what is going on in our skull. The authors used MR images to compare the relative volumes of the caudate nuclei as the caudate is a bilateral structure , and drew a connection between any asymmetries and symptoms of ADHD: "The degree of caudate asymmetry significantly predicted cumulative severity ratings of inattentive behaviors. Psychiatry Research. Physiol Rev. The caudate nucleus is a pair of brain structures that make up part of the basal ganglia. The smaller restricted striatocapsular infarct, also due to embolism as is the larger variety, usually does not give cortical signs and is an underacknowledged entity [5,6]. In this Page. S2CID Sinauer Associates; The caudate, however, is also thought to be involved with more than just motor function. The dorsal-prefrontal cortex subcortical loop involving the caudate nucleus has been linked to deficits in working memory, specifically in schizophrenic patients. Patients with Parkinson disease or other basal ganglia disorders such as Huntington disease in which caudate neurons themselves are damaged have deficits in other procedural learning tasks, such as the acquisition of new motor programs. The cognitive functions of the caudate nucleus. Similar articles in PubMed.

0 thoughts on “Caudate nucleus”