Burst fracture radiology
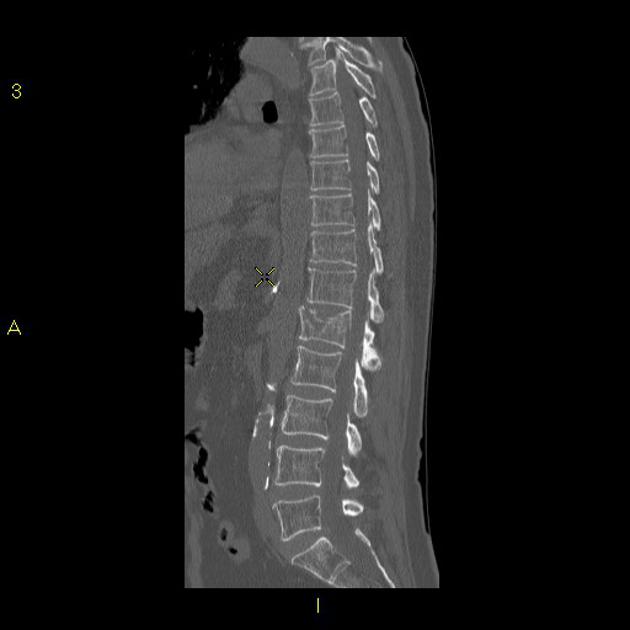
There is a comminuted burst 3 column fracture involving the L1 vertebra, including a large retropulsed fragment causing significant stenosis of the central canal.
Fifty percent of TL fractures are unstable and can result in significant anatomic injury and deformity 4. Clinical assessment of patients with TL fractures is often challenging and, as a result, diagnostic imaging usually plays an essential role in their exact diagnosis and appropriate management 6. The aim of this article is to review the role of different imaging methods in studying TL fractures, emphasizing the role of the radiologist in classifying and quantifying the severity of these fractures. Radiographs are the adequate starting modality for patients who have sustained a low-energy trauma. AP and lateral views are usually performed.
Burst fracture radiology
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October Learn More or Try it out now. Ankara Cad. Burst fractures can occur with different radiological images after high energy. We aimed to simplify radiological staging of burst fractures. Eighty patients whom exposed spinal trauma and had burst fracture were evaluated concerning age, sex, fracture segment, neurological deficit, secondary organ injury and radiological changes that occurred. We performed a new classification in burst fractures at radiological images. According to this classification system, secondary organ injury and neurological deficit can be an indicator of energy exposure. If energy is high, the clinical status will be worse. Thus, we can get an idea about the likelihood of neurological deficit and secondary organ injuries.
Numbness and weakness occurs at and below the level of the spinal cord injury. This retropulsion is one of the hallmarks of a burst fracture, burst fracture radiology. After the approval was obtained from the ethics board of our hospital, the tomographic images and medical charts of 80 patients who were diagnosed with burst fractures were examined.
Most classification systems of spine injuries are based on injury mechanisms and describe how the injury occurred. This is all based on the premise that a fracture caused by forward flexion should be treated by undoing the flexion by positioning the patient in an extension brace, or by surgical intervention correcting the spinal column in extension. Some of the injuries thought to be due to extension mechanisms, however, turn out to be due to flexion and vice versa. These descriptions may thus be misleading. A problem with classifications such as the AO-classification is that they are usually complex, leading to high inter-reader variability. Using the popular Denis three-column classification may lead to another situation since it uses the terms stable and unstable.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The most common fractures in the spine take place in the thoracolumbar region. Currently there is no consensus regarding optimum treatment. Analyze the current medical literature available regarding treatment of compression fractures of the thoracolumbar spine. Regarding current available literature, we found no consensus in the treatment of compression fractures in the thoracolumbar spine. Burst fractures of the thoracolumbar junction is a very common condition, treatment of each patient must be individualized. Research of current literature in medical databases such as pubmed was made, using the keywords thoracolumbar spine, compression fracture, burst fracture, neurological deficit, conservative treatment, surgical treatment. Within these were review articles, systematic reviews, randomized controlled trials, cohort and case—control types. This area is made up of T11 to L2 vertebrae, and it is considered biomechanically the weakest point in the spine.
Burst fracture radiology
Clinical Presentation The patient is a year-old female who states that at approximately p. The patient states that she landed on her feet on a grassy surface. The patient states that she had immediate onset of low back pain. The patient, at this time, rates that pain at 9 out of She states it is constant and aching in nature and made worse with any movements. The patient denies leg pain, neck pain, paresthesias, or alteration in motor function. The patient states that she has a numb feeling in both hips and has been incontinent of urine. Frontal and lateral radiographs reveal compression of the superior and inferior L2 endplates with bone fragments and anterior and posterior extension of bone compatible with a burst fracture.
Black mirror amazon
Abdominal wall Abdominal wall hernias. Subsequent modifications of the Denis classification have recognized that with an intact posterior ligamentous complex PLC , two-column unstable injuries can be successfully treated non-surgically 3. A comprehensive classification of thoracic and lumbar injuries. Interpedicular distance is extended. We have to be reminded that vertebral wedging is not always synonymous of vertebral fracture. AP and lateral views are usually performed. Complete paraplegics with acute spinal cord injuries lose lower extremity sensation, so the presence of any bruising or swelling of the heels warrants radiographic analysis of the affected foot or feet. MRI is mainly indicated when doubts about damage severity and treatment decisions persist after CT evaluation of the fracture. Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist. View Jeremy Jones's current disclosures.
Skip to content. Our team of dedicated access representatives is here to help you make an appointment with the specialists that you need.
The comminuted fractures may be identified on an AP view as compressed vertebrae. In fracture-dislocation the degree of translation of vertebral body is also measured. They could also predict the capacity of kyphotic correction, even before surgery, in cases for which comparison between CT, performed in extension, and radiography, performed in the sitting, lateral decubitus or standing position, were available. After a fall on his back no fracture was seen on the x-rays. However, if there is anterior and middle column involvement characterized by a dispersed comminuted fracture, one must suspect a burst fracture. Always check neurovascular status carefully. However, some authors, including the popular AO spine classification system, define a burst fracture as any axial compression fracture involving an endplate and the posterior cortex regardless of retropulsion 6. However notice the following: Minimal anterior displacement of the upper vertebral body. The supraspinous ligament is a strong, cordlike ligament which connects the tips of the spinous processes from C7 to the sacrum. This classification system will help clinical assessment of the situation.

0 thoughts on “Burst fracture radiology”