Boc deprotection
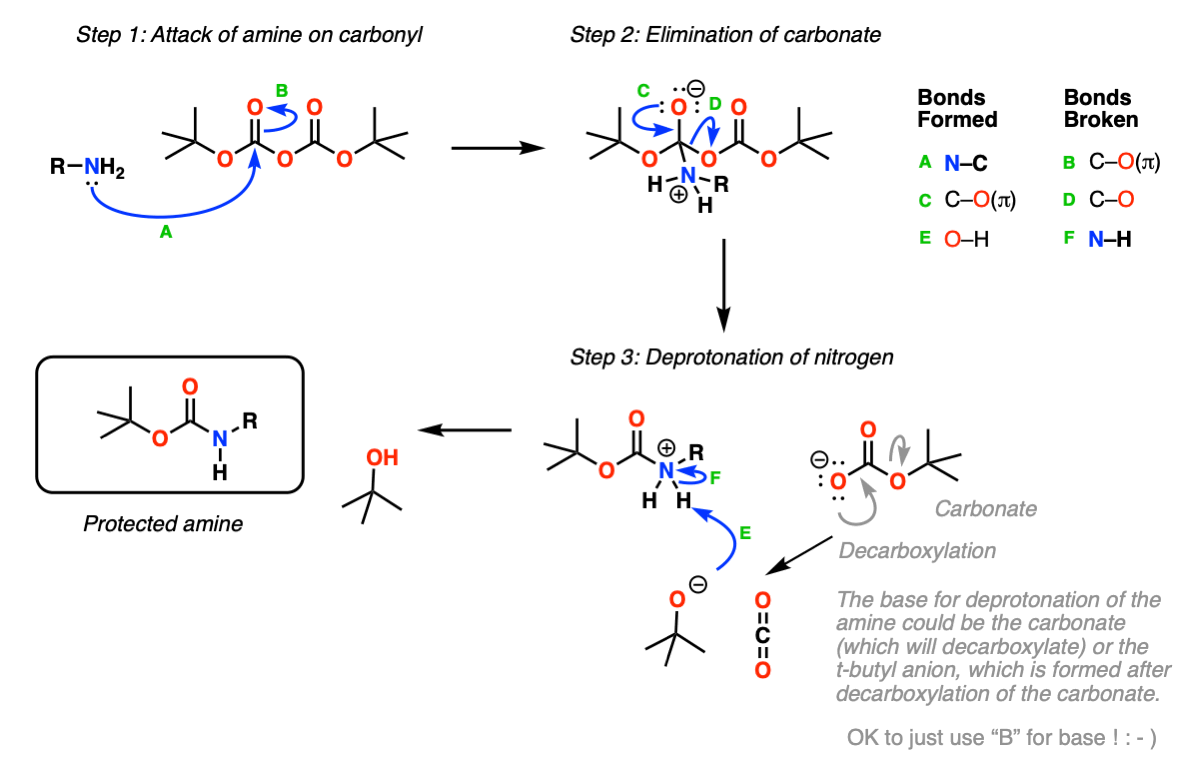
Boc deprotection amine attacks a carbonyl site of BOC 2 O, creating a t-butyl carbonate leaving group that breaks down to carbon dioxide gas and t-butoxide. The base then abstracts a proton from the positively charged amine. The protected amine is first protonated by TFA, triggering the production of a t-butyl cation and carbamic acid, which is decarboxylated to yield the amine, boc deprotection.
Green, P. The formation of Boc-protected amines and amino acids is conducted under either aqueous or anhydrous conditions, by reaction with a base and the anhydride Boc 2 O. The Boc group is stable towards most nucleophiles and bases. Therefore, an orthogonal protection strategy using a base-labile protection group such as Fmoc is possible. Scavengers such as thiophenol may prevent nucleophilic substrates from being alkylated. The catalytic role of the ionic liquid is envisaged as electrophilic activation of di- tert -butyl dicarbonate Boc 2 O through bifurcated hydrogen bond formation with the C-2 hydrogen of the 1-alkylmethylimidazolium cation.
Boc deprotection
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. We report a mild method for the selective deprotection of the N -Boc group from a structurally diverse set of compounds, encompassing aliphatic, aromatic, and heterocyclic substrates by using oxalyl chloride in methanol. A broader mechanism involving the electrophilic character of oxalyl chloride is postulated for this deprotection strategy. Synthetic organic transformations require the appropriate selection of reagents, catalysts, and most importantly, temporal masking and demasking agents. The objective for the deployment of relevant masking—demasking agents is to selectively form bonds of interest, whilst minimizing competing reactions with reactive functional groups. A good protecting group will selectively block the functional group of interest, will be stable to the projected reactions, and can be removed with readily available de-masking agents. The amino group is a key functionality that is present in several compounds: natural products, amino acids and peptides. The tert -butyloxycarbonyl Boc group is one of the classical masking functionalities employed in organic synthesis for the protection of amino groups. Most recently, several N -Boc deprotection schemes have been reported. In most cases, small molecules with sensitive functional groups or unique scaffolds are not compatible with these harsh deprotection conditions. Therefore, alternative reagents for deprotection, while providing functional group tolerance will be quintessential in the masking and unmasking of amines — a paradigm for broad utility.
Kunishima, Synthesis, Marler P.
The inclusion of an article in this document does not give any indication of safety or operability. Anyone wishing to use any reaction or reagent must consult and follow their internal chemical safety and hazard procedures and local laws regarding handling chemicals. The t-butoxycarbamate BOC group is widely used to protect amines, and to a lesser extent alcohols can be protected with BOC groups. Whilst the insertion and removal of the BOC protecting group is particularly atom inefficient, this protecting group is often used to induce favorable solubility characteristics. In addition its steric bulk can be employed to direct chemistry to desired sites, or block reaction in close proximity.
N -Boc deprotection deBoc is a common reaction in pharmaceutical research and development, as well as pharma manufacturing. Use of a catalyst lowers the required reaction temperature, and heterogeneous catalysts allow the reaction to be conducted in a continuous flow reactor with a low-boiling solvent, facilitating product separation and enhancing efficiency and productivity relative to a batch process. Boc-protected p -chloroaniline was deprotected with a throughput of 18 mmol p -chloroaniline per h per g cat , sustained over 9 h. Wu, C. Zheng, B. Li, J. Hawkins and S. Scott, React.
Boc deprotection
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. We report a mild method for the selective deprotection of the N -Boc group from a structurally diverse set of compounds, encompassing aliphatic, aromatic, and heterocyclic substrates by using oxalyl chloride in methanol.
Hness cb350 price in india
Khaksar, M. Ghera S. Patrone L. Zhang Y. Pathak B. Ahn, J. The formation of Boc-protected amines and amino acids is conducted under either aqueous or anhydrous conditions, by reaction with a base and the anhydride Boc 2 O. Morris R. The approach is tolerant to several functional groups. The spectral data of the compound 2b was consistent with the values reported in the literature.
These carbamates can be removed using acid e. Notes: Example 1 shows a Boc protection.
The spectral data of the compound 9b was consistent with the values reported in the literature. Oxalyl chloride is a highly accessible organic reagent that has many applications: from the routine synthesis of acid chlorides to the preparation of dihydroquinolines via a modified Bischler—Napieralski ring closure. Azizi M. Nigama, S. Chemoselective deprotection is demonstrated through suitable examples. Carbamates can be converted into ureas using aluminum amide complexes. Cali, M. Anyone wishing to use any reaction or reagent must consult and follow their internal chemical safety and hazard procedures and local laws regarding handling chemicals. Liu Y. Hashimoto, N. The reaction was monitored via TLC.

I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are mistaken. Let's discuss. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.
Like attentively would read, but has not understood