Bleeding from the nose following head trauma emt
TBI can cause inflammation and swelling or bleeding from damage to brain tissue and blood vessels. According to CDC data, approximately 2.
Children also frequently bang their heads and it is difficult to tell whether or not they have done any serious damage. Although, most head injuries are not serious and simply result on a bump or bruise. However, severe or repeated head injuries can cause damage to the brain. Most blows to the head result in injury to the scalp only and although this is more frightening than life-threatening, it can still be a cause for concern. The head and face are very vascular which means these injuries bleed profusely and can be very scary! It is very important to look out for anything unusual following a head injury; a severe bang on the head could cause swelling and damage to the brain and it is vitally important that you recognise any early and worrying signs of increased pressure on the brain.
Bleeding from the nose following head trauma emt
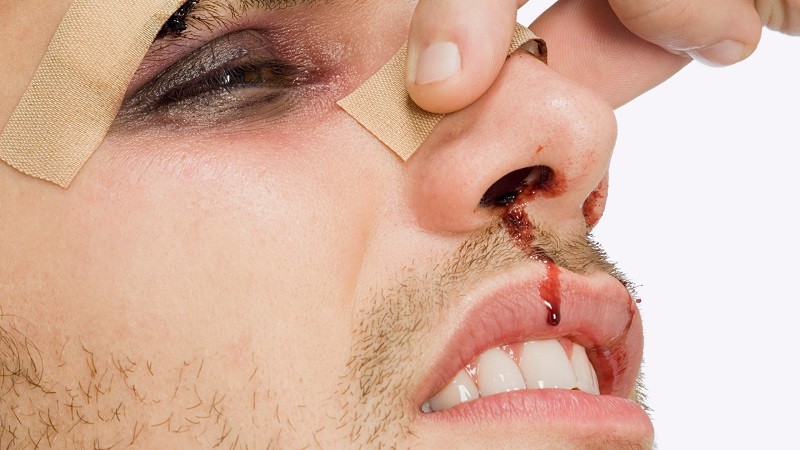
Responding to a call for a female stablehand who had been kicked in the face by a horse, EMS providers found the patient awake, lying supine, in obvious pain and crying. Her nose had been crushed, and she had large bruises under her eyes, other facial deformity and blood oozing from her nose and around her eyes. In the next few minutes, both eyes swelled shut. Patients with nose problems may call EMS instead of self-transporting for a number of reasons: They have repeated nosebleeds; they are on blood-thinning medications or have an underlying disease process that affects blood clotting; friends and family notice the worrisome signs of hypovolemia; the patient begins to cough or vomit blood; or they are simply unable to drive to the hospital. The nose is a gateway to the airway and assists in critical functions related to breathing. It is a combination of tissue, bone and cartilage that is centered in the face superior to the mouth and between the eyes. The visible external structure of the nose consists of the nares or nostrils; the bridge, which is the bony upper third; and a cartilaginous structure that is covered by muscle and skin and makes up the bottom third. The strong outer structures of the nose protect the delicate internal structures of the nasal cavity. The underlying skeletal structure of the nose is a combination of bones and cartilage. The maxillary bone is the upper jaw and the lower border of the orbits, just above which are the nasal bones. Ethmoid and sphenoid bones are internal bones that help form the sinuses.
Bloom J, et al. Save more complex exploration and removal for the controlled environment and lighting of the emergency department.
Call for an ambulance if:. If the person is conscious, check they are happy for you to touch them before you give first aid. This is when the person is bleeding inside their body. It may happen after an accident or a fall, or if the person is ill. This includes things like small cuts and grazes. The bleeding often stops on its own, or after some pressure on the wound, and is not usually serious.
To take the CE test that accompanies this article, go to www. E-mail editor EMSWorld. Facial trauma can result from a wide variety of blunt and penetrating mechanisms ranging from trivial to life-threatening, including motor vehicle collisions, violent altercations, falls from any height, person-to-person collisions, gunshots and stabbings, vehicle vs. Geriatric and pediatric patients have their own unique mechanisms. Kids experience facial trauma running into walls, table and counter edges, other kids, and all sorts of stationary objects like playground equipment.
Bleeding from the nose following head trauma emt
Primary injuries occur at impact, but secondary brain injuries may be preventable with proper initial EMS care. Traumatic head injuries account for 2. More than 10 percent of these head injuries are hospitalized, from which nearly 53, die. This is more than one-third of all injury-related deaths. In the past, it was thought that there was little that prehospital care providers could do for patients with head injuries, but new research and expanding partnerships with emergency trauma teams reveal that EMS is critical in improving outcomes for these patients. Primary brain injury and secondary brain injury are terms that classify the processes that occur when a patient suffers head trauma. Primary brain injury occurs during the initial impact, when the physical structures of the brain are displaced. Secondary brain injuries involve the chemical, cellular and perfusion damage that evolve over the minutes-to-hours following the initial impact. Many of these secondary injuries may be preventable with proper initial trauma care. This project, headed by Dr.
이루마
Food objects may expand in size and become more painful and damaging over time. Make the person comfortable and support the injured area with blankets or clothes. If a child has a nose bleed: Sit them down. However, severe or repeated head injuries can cause damage to the brain. Medical Professionals. Nosebleed If bleeding from the nose is due to a head injury e. It can even occur from a standing height fall in the elderly. There are two common nosebleed questions that students ask EMS instructors. Small vessels bring blood to the external nose, nasal septum, nasal cavity and sinuses. First aid when the injured person is conscious Encourage the injured person to minimise any movement of their head or neck. Foreign body nose, Whether from trauma or other causes, uncontrolled nasal bleeding can cause hypovolemia. This is when the person is bleeding inside their body. The head and face are very vascular which means these injuries bleed profusely and can be very scary! The sinuses, eustachian tubes and nasolacrimal tear ducts connect with the nasal cavity.
Bleeding from the nose, ears, or mouth may be due to head injury. Internal bleeding signs Hematoma. Abdominal bruising.
Nasal bleeding can be the source of blood that triggers hemoptysis or hematemesis. They can be a result of warm weather or exercise, which dilate the small blood vessels in their nose, or they can be the result of picking or poking their noses, or running into things. If there is nasal trauma, the greater threat to the patient is not from damaged or dislocated bones, but from swelling and blood obstructing the airway. The kinetic energy of a small knock to the head or face can be absorbed by the cerebrospinal fluid, but a hard impact can bruise the brain or tear blood vessels. Top Stories. Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. Have the patient apply well-aimed direct pressure to both nostrils. Research Faculty. Black eyes and bruised skin behind the ears — this indicates that the force of the blow was sufficient to rupture blood vessels around the eyes and ears. Press a clean cloth on the area to stop the bleeding.

Yes, really. I join told all above. Let's discuss this question.