Best cpu cooling paste
If you're building a high-end 14th-gen Intel platform computer, you'll want to make sure that your CPU's thermal performance is in check. This is where a high-quality thermal paste comes in handy.
WePC is reader-supported. When you buy through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission. Prices subject to change. Learn more. Thermal paste is often an overlooked component when configuring a new PC, either due to a lack of experience, or the convenience of coolers that come with pre-applied thermal paste. Opting to purchase and apply your own thermal paste during CPU installation is a wise choice for achieving better temperatures at both stock and overclocked speeds. Leaving thermal paste for too long can result in performance issues and gradual overheating , potentially harming your CPU in the long term.
Best cpu cooling paste
Choosing the best thermal paste may sound simple, but a dizzying array of options can turn this seemingly easy choice into a time-consuming and confusing task. Thermal paste is designed to minimize microscopic air gaps and irregularities between the surface of the cooler and the CPU's IHS integrated heat spreader , the piece of metal built into the top of the processor, to transfer heat to the CPU cooler. Good thermal paste can have a profound impact on your performance because it will allow your processor to transfer more of its waste heat to your cooler, keeping your processor running cool. Choosing the best thermal paste is also important if you plan on overclocking your rig to its fullest. Performance enthusiasts often swear by a favorite brand of paste, but new recipes crop up fairly frequently. We've extensively tested some of the top thermal pastes on the market. If you're hunting for more exotic pastes off the beaten path, we also have plenty of historical data below covering 90 different pastes and yes, we've even tested toothpaste. Thermal paste can go by many names, such as "thermal compound," "thermal grease," or "TIM" Thermal Interface Material , but they all have the same purpose — to help keep your chip cool by ensuring that heat passes efficiently from the CPU to the cooler. Most pastes are made of ceramic or metallic materials suspended within a proprietary binder, allowing for easy application and spread and simple cleanup. Depending on their specific formula, these thermal pastes can be electrically conductive or non-conductive. Electrically conductive thermal pastes can carry electricity between two points, meaning that if the paste squeezes out onto other components, it can cause damage to motherboards and CPUs when you switch on the power. A single drop out of place can lead to a dead PC, so extra care is imperative. Liquid metal compounds are almost always electrically conductive, so while these compounds perform better than their paste counterparts, they require more focus and attention during application. They are very hard to remove if you get some in the wrong place, which would fry your system.
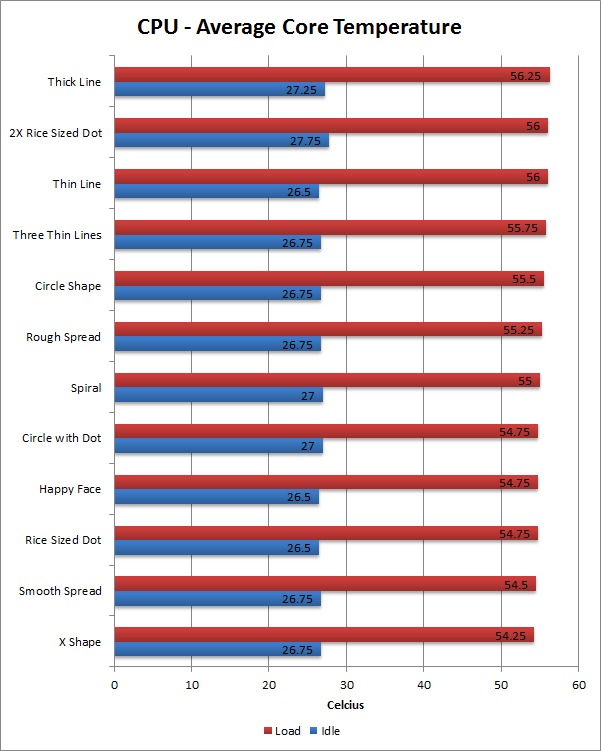
The results for gpu applications would be different though, as the more viscous pastes would have an edge here - at least from what I've read so far.
Aftermarket thermal paste can also drop your GPU temperatures, making thermal paste a vital part of every PC build. When it comes to thermal paste, thermal compound, thermal grease, or TIM thermal interface material , the cooling performance is the most critical part of the selection process, but it's not the end-all-be-all. Other features, such as ease of application, viscosity, and how easy it is to remove the paste from the CPU IHS integrated heat spreader that covers the CPU diealso play an important role. The best thermal paste doesn't have to achieve the absolute best thermal performance, especially if you're a regular user who doesn't plan to overclock their CPU. A quality budget paste is plenty for most users, even those owning one of the best CPUs on the market. You should consider getting a high-end grease or maybe even a liquid metal thermal compound only if you demand the lowest temperatures possible or are into overclocking.
Choosing the best thermal paste may sound simple, but a dizzying array of options can turn this seemingly easy choice into a time-consuming and confusing task. Thermal paste is designed to minimize microscopic air gaps and irregularities between the surface of the cooler and the CPU's IHS integrated heat spreader , the piece of metal built into the top of the processor, to transfer heat to the CPU cooler. Good thermal paste can have a profound impact on your performance because it will allow your processor to transfer more of its waste heat to your cooler, keeping your processor running cool. Choosing the best thermal paste is also important if you plan on overclocking your rig to its fullest. Performance enthusiasts often swear by a favorite brand of paste, but new recipes crop up fairly frequently. We've extensively tested some of the top thermal pastes on the market. If you're hunting for more exotic pastes off the beaten path, we also have plenty of historical data below covering 90 different pastes and yes, we've even tested toothpaste. Thermal paste can go by many names, such as "thermal compound," "thermal grease," or "TIM" Thermal Interface Material , but they all have the same purpose — to help keep your chip cool by ensuring that heat passes efficiently from the CPU to the cooler. Most pastes are made of ceramic or metallic materials suspended within a proprietary binder, allowing for easy application and spread and simple cleanup. Depending on their specific formula, these thermal pastes can be electrically conductive or non-conductive.
Best cpu cooling paste
Changes to the shape, size, and internal component layout of modern CPUs have made applying thermal paste, also known as thermal interface material TIM , more complicated than it used to be. CPUs have incorporated ever more cores. And despite shrinking manufacturing nodes, many processors have just gotten physically bigger. So while you used to be able to apply thermal paste basically the same way across all consumer manufacturers and platforms and expect great results, that's no longer the case. And let's face it: There was never any true consensus across the PC-building world about just what is the "right" or the "best" way of applying TIM. We all just know the wrong way when we see it. So at the risk of… verging into an area of hotly contested debate, we're here to offer some simple instructions on how to properly apply your thermal interface material of choice check our tested list of the best thermal paste between your CPU and cooler, to achieve good thermal transfer and get that pesky heat away from your components and outside your case. We're not saying the advice below is the absolute best method or the only correct method. We're just saying it works, and it's more or less what's recommended by PC thermal experts like Noctua and others.
Drain catcher
For the air cooling low- and high-tension tests, we used a large Noctua NH-D15 air cooler. It's also non-corrosive and electrically non-conductive, so your system is safe at all times. Your processor generates a lot of heat. Thermal Conductivity: 6. Most, but not all, traditional pastes are electrically non-conductive. When you make a purchase using links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission. The Thermal Grizzly Kryonaut is an impressive, high-end thermal grease made for extreme overclocking. Kryonaut utilizes its high thermal conductivity of Only a few minor changes to the pecking order have occurred, and these easily fall within the tight margins of standard deviation. Thermal Conductivity: 2. Nice comparison, thanks. It is important for several reasons:.
Aftermarket thermal paste can also drop your GPU temperatures, making thermal paste a vital part of every PC build.
Thermal Conductivity: Unlisted. Other viscous thermal compounds we recommend include the Thermalright TFX as well as our pick for the best laptop thermal paste, featured right below. Since the chip is bare, not covering a part with paste will create a dangerous hotspot that can lead to the chip frying itself. Arctic Silver Ceramique 2. If even a tiny drop of liquid metal comes into contact with a component that conducts electricity, it's game over for your CPU, GPU, or motherboard. Key Takeaways Thermal compounds might always be compared and debated over, but the simple fact remains: PC system building needs thermal compounds to effectively dissipate thermal loads. With low thermal resistance of 0. Direct die cooling is also the name of the game in laptops because, in notebooks, both the CPU and GPU chips lay bare without a heat spreader to cover them. Liquid metal can cause reactions with some metals, such as aluminum, and some reports of reactions with copper are also documented by end-users. Most, but not all, traditional pastes are electrically non-conductive. The Corsair XTM50 is a premium choice which comes with an application kit as well for a hassle-free experience. Spreading the compound is made easier with cotton swabs and generous pressure to develop a consistent coating on the CPU IHS. Thermal Grizzly Conductonaut is a liquid metal-based thermal compound designed for experienced users who want to push the boundaries of cooling performance. Water coolers work on a similar principle. Arctic MX

Very useful phrase
It is remarkable, the valuable information