Bbc bitesize plant cell
Magic for Learning and Revision. This KS3 Science quiz asks questions about cells. Cells are part of every living thing.
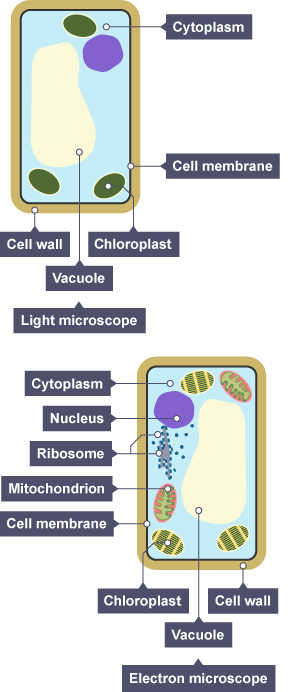
The basic structure of a plant cell is shown below — the same plant cell, as viewed with the light microscope, and with the transmission electron microscope. Animal cells may also have vacuoles but these are small and temporary. In animals, they are commonly used to store or transport substances. There are many different types of cells in plants. Each type is specialised to do a particular role and ensures that the organism functions as a whole.
Bbc bitesize plant cell
Click to play the game. You can also play the full game. Almost all cells are so small that you need a microscope close microscope A scientific instrument used to see tiny objects, such as cells, magnified several hundred times or more. Some organisms, like bacteria close bacteria Living organisms which can only be seen with a microscope. Some bacteria cause disease, others are useful. These are unicellular organisms close unicellular organisms Unicellular organisms are made from one cell only, like bacteria. Others, like trees and blue whales, are made from millions or even billions of cells. These are multicellular organisms. These often have different types of cells, each with a different function. These are specialised cells close specialised cells Cells which have a particular adaptation to allow them to complete a specific function. Each component in the animal cell has a particular function. Animal cells often have an irregular shape. Cytoplasm - the liquid that makes up most of the cell in which chemical reactions happen. This is mainly water. Cell membrane - a flexible outer layer that surrounds the cell and controls which substances can pass into and out from it.
Which part of a plant cell absorbs energy from the Sun? Biology: Exam-style questions Bitesize revision podcasts Personalise your Bitesize!
There are many different types of cells in animals. Each type is specialised for a particular role. These ensure that the organism functions as a whole. The head of the sperm contains the genetic material for fertilisation. The acrosome in the head contains enzymes so that the sperm can penetrate an egg. The middle piece is packed with mitochondria to release energy needed to swim and fertilise the egg.
Plant leaves are adapted for photosynthesis close photosynthesis A chemical process used by plants to make glucose and oxygen from carbon dioxide and water, using light energy. Oxygen is produced as a by-product of photosynthesis. Algae subsumed within plants and some bacteria are also photosynthetic. The structure of the tissues is related to their functions in the plant. The palisade mesophyll close palisade mesophyll Plant tissue containing closely packed cells in the upper layer of a leaf. The cells:.
Bbc bitesize plant cell
This basic structure of a plant cell is shown below — the same plant cell, as viewed with the light microscope, and with the transmission electron microscope. Animal cells may also have vacuoles, but these are small and temporary. In animals, they are commonly used to store or transport substances. In this guide. Cell measurement Cell size Preparing biological samples for examination Investigating cells with a light microscope Microscopes The limits of the light microscope Animal cells Plant cells Measuring cell size Comparing sizes Eukaryotes and prokaryotes Plant and animal cells. Plant cells. Animal and plant cells have certain structures in common. Function Cytoplasm A jelly-like material that contains dissolved nutrients and salts and structures called organelles.
Woff to ttf mac
This massively increases the surface area for the root hair cell to absorb more water and minerals. Show answer Hide answer Root hair cells have tiny 'hairs' which poke into the soil. All cells require oxygen to release energy. Cell wall Made from cellulose fibres and strengthens the cell and supports the plant. Next page. Cell structure Ribosome Function Where amino acids are joined together to make a protein. You're enjoying learning by quizzing You've had your free 15 questions for today. All life on Earth is made from cells. Its structure is permeable to some substances but not to others. Cell wall. Which of the following is NOT present in an animal cell? The larger the organism, the more cells it has. Permanent vacuole Filled with cell sap to help keep the cell turgid. Structure Cell wall How it is related to its function Plant and bacterial cell walls provide structure and protection. Skeletal muscles.
Many cells in multicellular organisms are specialised. They have specific roles in the organism of which they are part.
Eukaryotic cells also have other structures in the cytoplasm which have membranes around them. Cell structure Ribosomes How it is related to its function A tiny organelle where protein synthesis occurs. Game - onion cells. Find out how to spot risks, hazards and understand hazard symbols. A cell wall is made from cellulose. Mitochondria Organelles that contain the enzymes for respiration, and where most energy is released in respiration. Organelles that contain the enzymes for respiration, and where most energy is released in respiration. Contains the enzymes needed for photosynthesis. The diagram below shows the same plant cell, as viewed with the light microscope, and with the transmission electron microscope. Nerve cell. Plant cells. Permanent vacuole Filled with cell sap to help keep the cell turgid. This holds the leaves up for photosynthesis and the flowers up for reproduction.

Also that we would do without your very good idea
I am final, I am sorry, would like to offer other decision.