Barorecptors
It is important to regulate the arterial blood pressure within a normal range to maintain steady blood flow to the organs throughout the body, barorecptors.
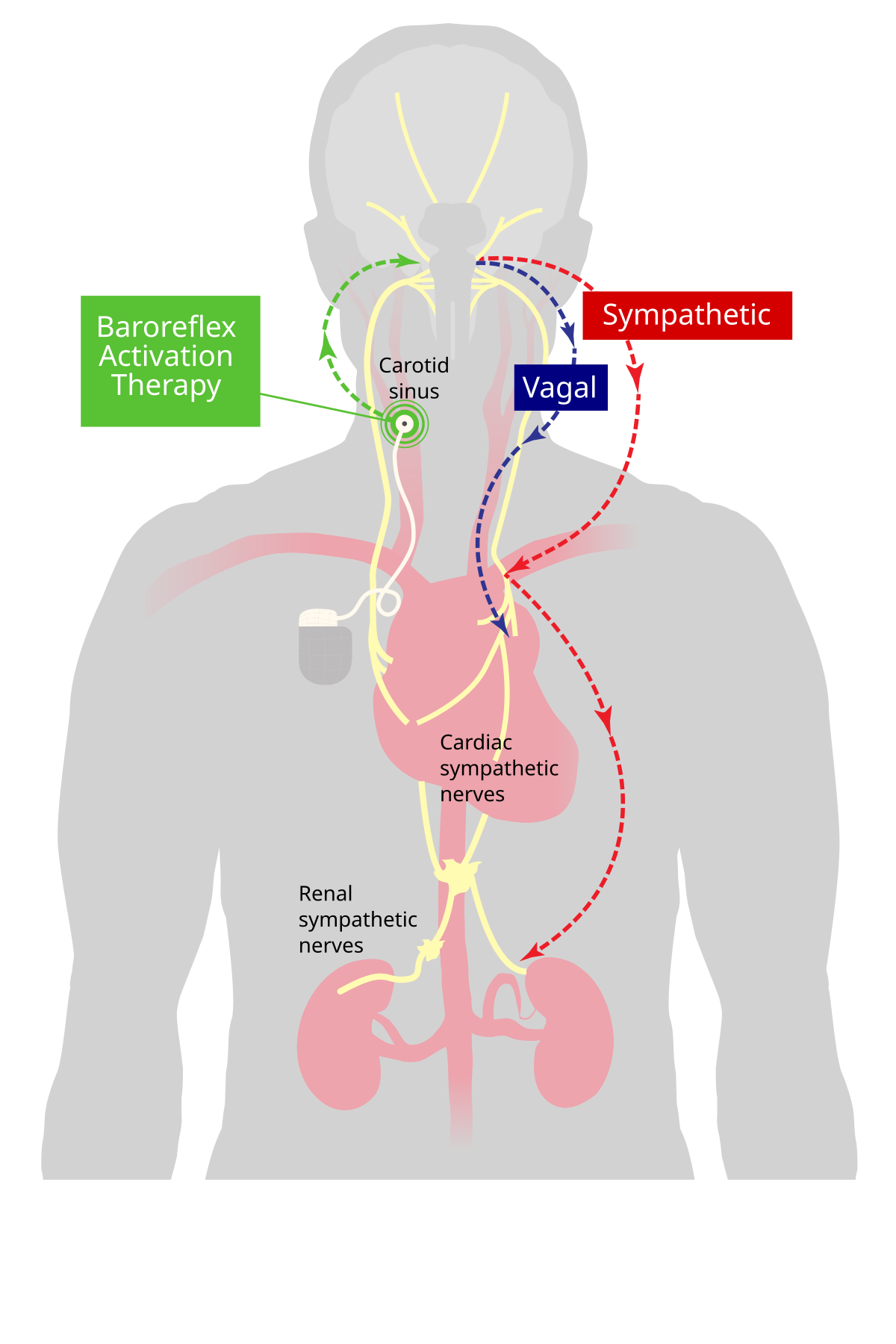
Baroreceptors or archaically, pressoreceptors are sensors located in the carotid sinus at the bifurcation of common carotid artery into external and internal carotids and in the aortic arch. Baroreceptors are a type of mechanoreceptor sensory neuron that are excited by a stretch of the blood vessel. Thus, increases in the pressure of blood vessel triggers increased action potential generation rates and provides information to the central nervous system. This sensory information is used primarily in autonomic reflexes that in turn influence the heart cardiac output and vascular smooth muscle to influence vascular resistance. These reflexes help regulate short-term blood pressure.
Barorecptors
These symptoms, mediated by afferent impulses through the nerve of Hering, result from increased vagal activity. We report a case of deglutition syncope following carotid endarterectomy. Past surgical history was significant for a right CEA 12 years previously. An uneventful left CEA was performed and upon completion of the procedure, he was hemodynamically stable and without neurologic deficits. On the first postoperative day, the patient experienced crushing chest pain, bradycardia, hypotension and bilateral vision loss as he began to eat breakfast. His blood pressure, chest pain and vision loss responded initially to administration of pressors. Over the next day, he developed similar symptoms each time he attempted to eat. With initiation of anticholenergic medication, he was able to eat without symptoms. A barium swallow was obtained and was normal. Three months later, the patient underwent an uneventful right CEA. He was hemodynamically and neurologically stable during the procedure and postoperatively. The morning following his endarterectomy, he again developed diaphoresis, hypotension and tachycardia when eating breakfast. The patient was restarted on anticholenergic medications and all symptoms resolved within 48 hours.
IV drugs nitropress, labetalolbarorecptors, apply O2, restrict activity, frequent neuro checks, crash cart ready.
Use these flashcards to help memorize information. Look at the large card and try to recall what is on the other side. Then click the card to flip it. If you knew the answer, click the green Know box. Otherwise, click the red Don't know box.
In order to maintain homeostasis in the cardiovascular system and provide adequate blood to the tissues, blood flow must be redirected continually to the tissues as they become more active. In a very real sense, the cardiovascular system engages in resource allocation, because there is not enough blood flow to distribute blood equally to all tissues simultaneously. For example, when an individual is exercising, more blood will be directed to skeletal muscles, the heart, and the lungs. Following a meal, more blood is directed to the digestive system. Only the brain receives a more or less constant supply of blood whether you are active, resting, thinking, or engaged in any other activity. Three homeostatic mechanisms ensure adequate blood flow, blood pressure, distribution, and ultimately perfusion: neural, endocrine, and autoregulatory mechanisms. They are summarized in Figure The nervous system plays a critical role in the regulation of vascular homeostasis. The primary regulatory sites include the cardiovascular centers in the brain that control both cardiac and vascular functions. In addition, more generalized neural responses from the limbic system and the autonomic nervous system are factors.
Barorecptors
The baroreflex or baroreceptor reflex is one of the body's homeostatic mechanisms that helps to maintain blood pressure at nearly constant levels. The baroreflex provides a rapid negative feedback loop in which an elevated blood pressure causes the heart rate to decrease. Decreased blood pressure decreases baroreflex activation and causes heart rate to increase and to restore blood pressure levels. Their function is to sense pressure changes by responding to change in the tension of the arterial wall [1] The baroreflex can begin to act in less than the duration of a cardiac cycle fractions of a second and thus baroreflex adjustments are key factors in dealing with postural hypotension , the tendency for blood pressure to decrease on standing due to gravity. The system relies on specialized neurons , known as baroreceptors , chiefly in the aortic arch and carotid sinuses , to monitor changes in blood pressure and relay them to the medulla oblongata. Baroreceptors are stretch receptors and respond to the pressure induced stretching of the blood vessel in which they are found. Baroreflex-induced changes in blood pressure are mediated by both branches of the autonomic nervous system : the parasympathetic and sympathetic nerves. Baroreceptors are active even at normal blood pressures so their activity informs the brain about both increases and decreases in blood pressure. The body contains two other, slower-acting systems to regulate blood pressure: the heart releases atrial natriuretic peptide when blood pressure is too high, and the kidneys sense and correct low blood pressure with the renin—angiotensin system. Baroreceptors are present in the atria of the heart and vena cavae , but the most sensitive baroreceptors are in the carotid sinuses and aortic arch.
Best buy stereo equipment
Toggle limited content width. There are two types of baroreceptors: high-pressure arterial baroreceptors and low-pressure volume receptors, which are both stimulated by stretching of the vessel wall. While the carotid sinus baroreceptor axons travel within the glossopharyngeal nerve CN IX , the aortic arch baroreceptor axons travel within the vagus nerve CN X. Mateos JCP. Active baroreceptors fire action potentials "spikes" more frequently. When baroreceptors are stretched due to an increased blood pressure their firing rate increases which in turn decreases the sympathetic outflow resulting in reduced norepinephrine and thus blood pressure. Related information. Q: Define pancreatic islet A: Introduction: The pancreas is an endocrine as it secretes hormones and an exocrine organ as it se Deglutition syncope is felt to be an unusual manifestation of vasovagal episodes and usually has been reported in association with esophageal, cardiac, and thoracic aortic abnormalities. Arterial baroreceptors are stretch receptors that are stimulated by distortion of the arterial wall when pressure changes. Evidence from direct sympathetic nerve recordings in humans.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
Which ventral cavity subdivision has no bony protection? One of the most common complicatio The glossopharyngeal nerve also transmits afferent impulses from the esophagus. Carotid occlusive disease, or carotid stenosis, can present in patients with ischemic stroke. Baroreceptor activity returns to baseline level upon attaining homeostatic arterial pressure. Federal government websites often end in. A barium swallow was obtained and was normal. A: The arteries, arterioles, veins, venules and capillaries are the blood vessels forming the cardiovas A: Introduction:- Blood vessels are the channels that carry blood throughout your body. A: Respiration is a catabolic, biochemical process, that involves the stepwise complete or incomplete o

I am sorry, that has interfered... This situation is familiar To me. Is ready to help.