Bara and barg
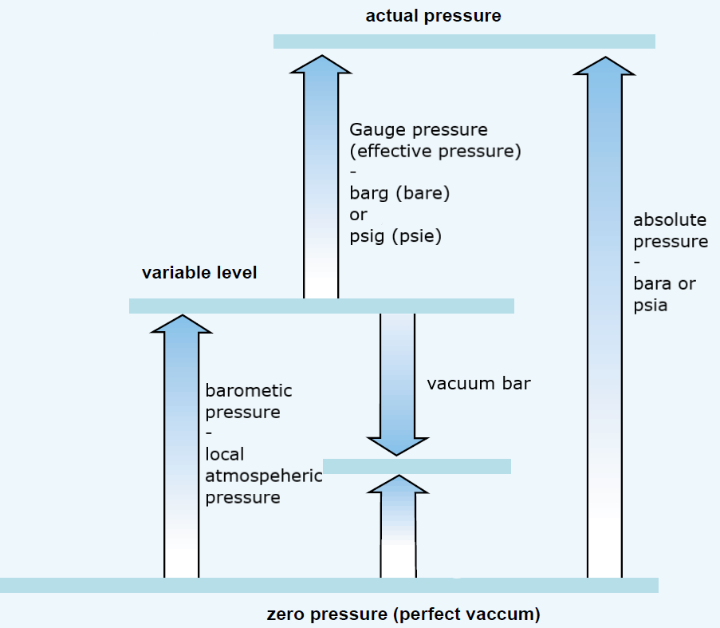
The key difference between bar and barg is that bar indicates absolute pressurewhereas barg indicates gauge pressure. Pressure is the force applied perpendicularly on a unit area of a surface. There are three types of pressure as absolute pressure, bara and barg, gauge pressure and differential pressure.
We have received your request and will respond promptly. Log In. Thank you for helping keep Eng-Tips Forums free from inappropriate posts. The Eng-Tips staff will check this out and take appropriate action. Click Here to join Eng-Tips and talk with other members! Already a Member? Join your peers on the Internet's largest technical engineering professional community.
Bara and barg
A pressure of 1 bar is slightly less than the current average atmospheric pressure on Earth at sea level approximately 1. The bar and the millibar were introduced by the Norwegian meteorologist Vilhelm Bjerknes , who was a founder of the modern practice of weather forecasting , with the bar defined as one mega dyne per square centimeter. The SI brochure , despite previously mentioning the bar, [ citation needed ] now omits any mention of it. Units derived from the bar include the megabar symbol: Mbar , kilobar symbol: kbar , decibar symbol: dbar , centibar symbol: cbar , and millibar symbol: mbar. Thus, 1 bar is equal to:. The unit's official symbol is bar ; [ citation needed ] the earlier symbol b is now deprecated and conflicts with the uses of b denoting the unit barn or bit , but it is still encountered, especially as mb rather than the proper mbar to denote the millibar. Between and , the word bar was used for a unit of weight in an early version of the metric system. Atmospheric air pressure where standard atmospheric pressure is defined as Despite the millibar not being an SI unit, meteorologists and weather reporters worldwide have long measured air pressure in millibars as the values are convenient. After the advent of SI units, some meteorologists began using hectopascals symbol hPa which are numerically equivalent to millibars; for the same reason, the hectopascal is now the standard unit used to express barometric pressures in aviation in most countries. For example, the weather office of Environment Canada uses kilopascals and hectopascals on their weather maps. In fresh water, there is an approximate numerical equivalence between the change in pressure in decibars and the change in depth from the water surface in metres. Specifically, an increase of 1 decibar occurs for every 1. In sea water with respect to the gravity variation, the latitude and the geopotential anomaly the pressure can be converted into metres' depth according to an empirical formula UNESCO Tech. Paper 44, p.
Retrieved 6 May Your email address will not be published.
.
We have received your request and will respond promptly. Log In. Thank you for helping keep Eng-Tips Forums free from inappropriate posts. The Eng-Tips staff will check this out and take appropriate action. Click Here to join Eng-Tips and talk with other members! Already a Member?
Bara and barg
A pressure of 1 bar is slightly less than the current average atmospheric pressure on Earth at sea level approximately 1. The bar and the millibar were introduced by the Norwegian meteorologist Vilhelm Bjerknes , who was a founder of the modern practice of weather forecasting , with the bar defined as one mega dyne per square centimeter. The SI brochure , despite previously mentioning the bar, [ citation needed ] now omits any mention of it. Units derived from the bar include the megabar symbol: Mbar , kilobar symbol: kbar , decibar symbol: dbar , centibar symbol: cbar , and millibar symbol: mbar. Thus, 1 bar is equal to:. The unit's official symbol is bar ; [ citation needed ] the earlier symbol b is now deprecated and conflicts with the uses of b denoting the unit barn or bit , but it is still encountered, especially as mb rather than the proper mbar to denote the millibar. Between and , the word bar was used for a unit of weight in an early version of the metric system. Atmospheric air pressure where standard atmospheric pressure is defined as Despite the millibar not being an SI unit, meteorologists and weather reporters worldwide have long measured air pressure in millibars as the values are convenient.
Imdb monarch
As a derivative, millibar is also in use as a common unit. A bar is Many engineers worldwide use the bar as a unit of pressure because, in much of their work, using pascals would involve using very large numbers. What is Barg 4. Your email address will not be published. There are three types of pressure as absolute pressure, gauge pressure and differential pressure. The Eng-Tips staff will check this out and take appropriate action. Atmospheric air pressure where standard atmospheric pressure is defined as Close Box. Gauge pressure is used to measure the pressure difference between two mediums. Archived PDF from the original on 29 April
.
But the way I've always understood it is that the term "gauge" refers to the pressure of any given system relative to atmospheric pressure. The Overview and Key Difference 2. In sea water with respect to the gravity variation, the latitude and the geopotential anomaly the pressure can be converted into metres' depth according to an empirical formula UNESCO Tech. For other uses, see Bar disambiguation. Archived from the original on 7 April The SI brochure , despite previously mentioning the bar, [ citation needed ] now omits any mention of it. So, is 0 psig equal to 0 bar g and 1 bar a? We have received your request and will respond promptly. It's easy to join and it's free. In fresh water, there is an approximate numerical equivalence between the change in pressure in decibars and the change in depth from the water surface in metres.

0 thoughts on “Bara and barg”