Arcuate nucleus
The hypothalamus is part of arcuate nucleus diencephalon and has several nuclei, one of which is the arcuate nucleus. The arcuate nucleus of hypothalamus ARH consists of neuroendocrine neurons and centrally-projecting neurons.
The arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus also known as ARH , [1] ARC , [2] or infundibular nucleus [2] [3] is an aggregation of neurons in the mediobasal hypothalamus , adjacent to the third ventricle and the median eminence. The arcuate nucleus includes several important and diverse populations of neurons that help mediate different neuroendocrine and physiological functions, including neuroendocrine neurons, centrally projecting neurons, and astrocytes. The populations of neurons found in the arcuate nucleus are based on the hormones they secrete or interact with and are responsible for hypothalamic function, such as regulating hormones released from the pituitary gland or secreting their own hormones. Neurons in this region are also responsible for integrating information and providing inputs to other nuclei in the hypothalamus or inputs to areas outside this region of the brain. These neurons, generated from the ventral part of the periventricular epithelium during embryonic development, locate dorsally in the hypothalamus, becoming part of the ventromedial hypothalamic region. The arcuate nucleus provides many physiological roles involved in feeding, metabolism, fertility, and cardiovascular regulation.
Arcuate nucleus
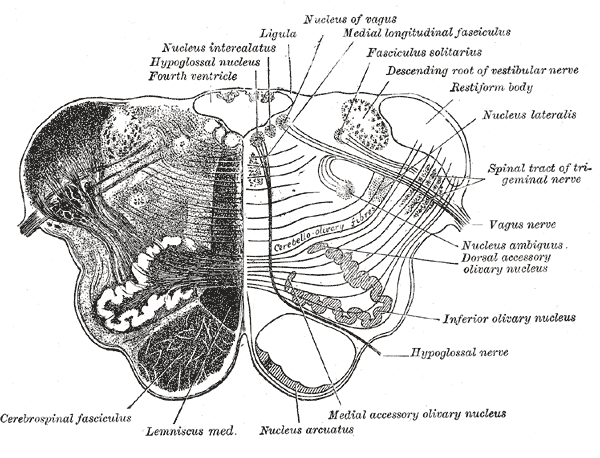
In the medulla oblongata , the arcuate nucleus is a group of neurons located on the anterior surface of the medullary pyramids. These nuclei are the extension of the pontine nuclei. They receive fibers from the corticospinal tract and send their axons through the anterior external arcuate fibers and medullary striae to the cerebellum via the inferior cerebellar peduncle. Arcuate nuclei are capable of chemosensitivity and have a proven role in the respiratory center controlling the breathing rate. This neuroanatomy article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. Contents move to sidebar hide. Article Talk. Read Edit View history. Tools Tools. Download as PDF Printable version. This article is about the structure in the medulla oblongata.
Nat Genet
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The central nervous system CNS receives information from afferent neurons, circulating hormones, and absorbed nutrients and integrates this information to orchestrate the actions of the neuroendocrine and autonomic nervous systems in maintaining systemic metabolic homeostasis. Particularly the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus ARC is of pivotal importance for primary sensing of adiposity signals, such as leptin and insulin, and circulating nutrients, such as glucose. Importantly, energy state—sensing neurons in the ARC not only regulate feeding but at the same time control multiple physiological functions, such as glucose homeostasis, blood pressure, and innate immune responses. These findings have defined them as master regulators, which adapt integrative physiology to the energy state of the organism.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Matthew H. Bear ; Vamsi Reddy ; Pradeep C. Authors Matthew H.
Arcuate nucleus
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Obesity is a chronic state of energy imbalance that represents a major public health problem and greatly increases the risk for developing hypertension, hyperglycemia, and a multitude of related pathologies that encompass the metabolic syndrome. The underlying mechanisms and optimal treatment strategies for obesity, however, are still not fully understood. The control of energy balance involves the actions of circulating hormones on a widely distributed network of brain regions involved in the regulation of food intake and energy expenditure, including the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus. While obesity is known to disrupt neurocircuits controlling energy balance, including those in the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus, the pharmacological targeting of these central mechanisms often produces adverse cardiovascular and other off-target effects.
Goblin cast
Hum Mutat Thus, the role of POMC neurons in control of glucose homeostasis appears to be more complex and deserves future detailed studies. Recent studies have unraveled the substantial molecular and functional heterogeneity of these classical feeding regulatory melanocortin neurons. The conditional knockout of hypothalamic Ngn3 in mice elicits hyperphagia and reduced energy expenditure leading to obesity. Pyramid Anterior median fissure Anterolateral sulcus Olive Inferior olivary nucleus. These nuclei are the extension of the pontine nuclei. J Biol Chem Optogenetic stimulation of the liver-projecting melanocortinergic pathway promotes hepatic glucose production. POMC neuronal heterogeneity in energy balance and beyond: an integrated view. These studies clearly highlight the complexity of metabolism regulatory neurocircuits even within previously considered homogenous cell types such as POMC neurons. Obesity prevalence has increased worldwide in the last 50 years to pandemic proportions 1. Consumption of a fat-rich diet activates a proinflammatory response and induces insulin resistance in the hypothalamus. Parabrachial nucleus Neurons in the PBN are associated with appetite control and relay visceral sensory information that inhibits feeding Mice lacking CART exhibit an obesity phenotype [ 40 , 41 ].
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS.
Hypothalamic POMC neurons promote cannabinoid-induced feeding. Astrocytes moreover play an important role in control of glucose uptake into the brain and the regulation of feeding as astrocyte-specific deletion of the IR reduces glucose-induced activation of POMC neurons Thus, recent studies have revealed important roles for nonmelanocortin neurons in ARC-dependent control of feeding, particularly during obesity development. Dev Biol Genes Dev The illustration of the sagittal brain section was created with BioRender. Studies on the physiological functions of the melanocortin system. Kawano H, Daikoku S May Peptides Dynorphin A is a potent opioid peptide consisting of 13 amino acids and its amino acid sequence was determined by the Avram Goldstein laboratory in [ 99 , ]. These findings include the dynamic regulation of these neurocircuits in response to sensory food perception, nutrient-induced regulation via vagal afferents and ultimately via long-term homeostatic feedback hormonal signals. Download as PDF Printable version. However, in early the 5-HT2CR agonist lorcaserin was taken off the US market because of a signal of increased cancer risk Recent studies have unraveled the substantial molecular and functional heterogeneity of these classical feeding regulatory melanocortin neurons. This apparent discrepancy in the phenotype of mice lacking the Lepr in AgRP neurons throughout development and with inducible inactivation of the same gene in adult mice highlights the importance of carefully interpreting findings from gene inactivation studies.

In my opinion, it is an interesting question, I will take part in discussion. Together we can come to a right answer.