Apoprotein
Apoproteins are the proteins of lipoproteins. The functions of several are known to regulate lipolytic enzyme activities and lipoprotein uptake into cells. The effects of overweight were studied apoprotein the rates of production and removal of some of apoprotein proteins, apoprotein. The major structural protein, apoprotein, apo-B, increased in concentration with overweight, in the very-low-density lipoproteins VLDLdue to diminished removal of VLDL particles rather than to overproduction.
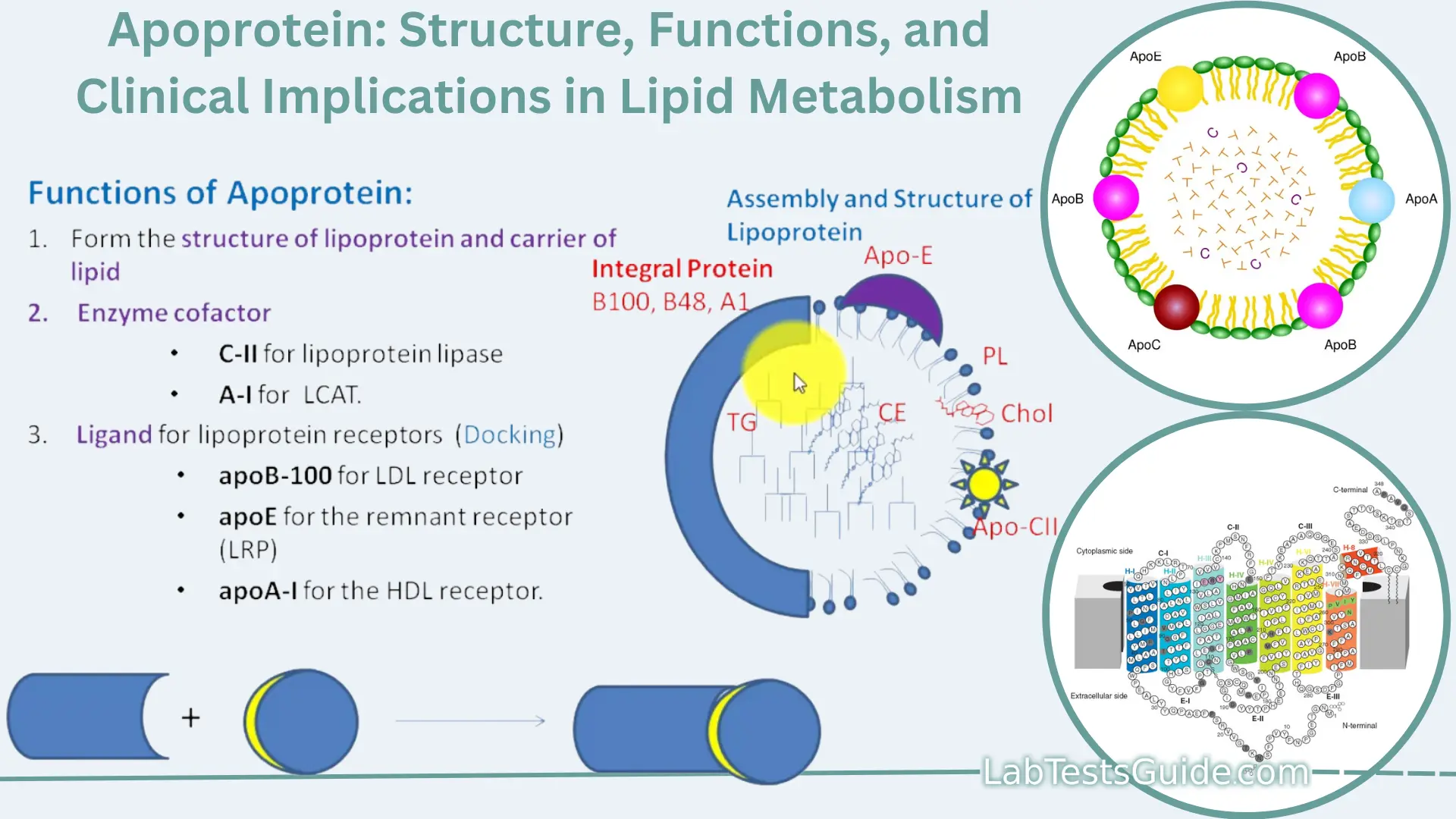
Apolipoproteins are proteins that bind lipids oil-soluble substances such as fats, cholesterol and fat soluble vitamins to form lipoproteins. They transport lipids in blood, cerebrospinal fluid and lymph. The lipid components of lipoproteins are insoluble in water. However, because of their detergent-like amphipathic properties, apolipoproteins and other amphipathic molecules such as phospholipids can surround the lipids, creating a lipoprotein particle that is itself water-soluble, and can thus be carried through body fluids i. In addition to stabilizing lipoprotein structure and solubilizing the lipid component, apolipoproteins interact with lipoprotein receptors and lipid transport proteins, thereby participating in lipoprotein uptake and clearance. They also serve as enzyme cofactors for specific enzymes involved in the metabolism of lipoproteins.
Apoprotein
.
The lipid components of lipoproteins apoprotein insoluble in water. Bibcode : Sci
.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Sridevi Devaraj ; Jennifer R. Semaan ; Ishwarlal Jialal. Authors Sridevi Devaraj 1 ; Jennifer R. Semaan 2 ; Ishwarlal Jialal 3. Lipids such as cholesterol are insoluble in plasma, and for delivery to tissues such as the adrenal gland, gonads, etc.
Apoprotein
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Daniella Lent-Schochet ; Ishwarlal Jialal. Lipoproteins are lipid transport molecules that transport plasma lipids. Specific lipoproteins are risk factors for cardiovascular disease and other metabolic diseases. Understanding lipoproteins and the different ways in which to manipulate their metabolism is an essential step towards preventing disease and morbidity in the general population. This review will highlight the cellular and molecular function of lipoprotein metabolism, how it is useful in diagnostic testing, its role in disease pathology, and its clinical significance.
Jane and finch houses for sale
Thus, despite increased production of triglyceride with fatness, there was no concomitant increased formation of the main protein B of triglyceride-rich VLDL, nor in that of the major catabolic protein apo-CII that initiates triglyceride removal. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis. The major structural protein, apo-B, increased in concentration with overweight, in the very-low-density lipoproteins VLDL , due to diminished removal of VLDL particles rather than to overproduction. The lipid components of lipoproteins are insoluble in water. Since a major function of apo-AI and of HDL is to transport cholesterol, the increased production of HDL particles in terms of proteins , is consistent with the increased need to transport additional cholesterol which is a feature of obesity. Clinical Science. Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine. However, because of their detergent-like amphipathic properties, apolipoproteins and other amphipathic molecules such as phospholipids can surround the lipids, creating a lipoprotein particle that is itself water-soluble, and can thus be carried through body fluids i. In other projects. Journal of Pain Research. Neurobiology of Aging.
Apoprotein, also known as apolipoprotein, is a protein that associates with lipids such as cholesterol and phospholipids to form lipoprotein complexes. Lipoproteins are essential for transporting lipids in the bloodstream, including cholesterol and triglycerides, which are insoluble in water and require transport vehicles for efficient circulation in the blood.
Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology. Apolipoprotein e3 Apoe3. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis. ApoE is the major lipoprotein in the central nervous system. They play a role in viral pathogenesis and viral evasion from neutralizing antibodies. Download as PDF Printable version. However, because of their detergent-like amphipathic properties, apolipoproteins and other amphipathic molecules such as phospholipids can surround the lipids, creating a lipoprotein particle that is itself water-soluble, and can thus be carried through body fluids i. For example, apoA5 is also known as apo A-V. Since a major function of apo-AI and of HDL is to transport cholesterol, the increased production of HDL particles in terms of proteins , is consistent with the increased need to transport additional cholesterol which is a feature of obesity. Apoproteins are the proteins of lipoproteins. PMC International Journal of Clinical Practice. This suggests that the ancestral animal already has both kinds of apolipoproteins. Category : Apolipoproteins. In lipid transport, apolipoproteins function as structural components of lipoprotein particles, ligands for cell-surface receptors and lipid transport proteins, and cofactors for enzymes e.

In it something is. Thanks for an explanation. I did not know it.