Allen brain atlas
Our focus on neuroscience began with the launch of the Allen Institute for Brain Science inwhich led to the creation of the widely-used Allen Brain Atlases.
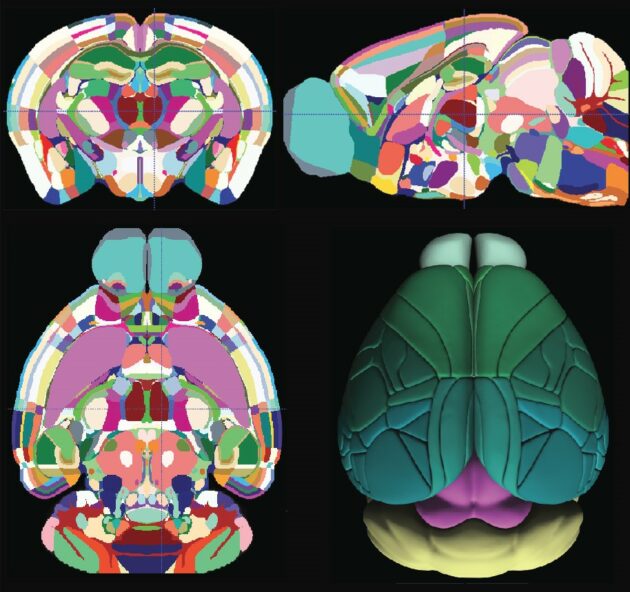
The Allen mouse brain atlas is a comprehensive digital resource that provides detailed information on the structure and function of the mouse brain. The Allen Mouse Brain Common Coordinate Framework is the backbone of spatially-focused workflows and tools that support spatial registration of new data to the atlas framework, semi-automatic analyses using the brain region hierarchy and delineations, and visualisation of extracted data in 3D. The atlas is incorporated in the QuickNII tool for spatial registration of serial 2D images, and employed in the QUINT workflow for extracting and quantifying labelled objects from images registered to the atlas. Originally built as a backend service for the interactive atlas viewer siibra-explorer, the API has been documented for connecting the brain atlases to other applications and web services. Sign up now for complete access to our tools and services. All tools and software Mouse Brain Atlas Overview.
Allen brain atlas
Six years and 32 million cells later, scientists have created the first full cellular map of a mammalian brain. In a set of 10 papers in Nature today, a network of researchers unveiled an atlas cataloging the location and type of every cell in the adult mouse brain. This relationship underscores how location shapes function, offering clues into the evolutionary history and intricate interactions of different brain regions. While the ancient ventral part features a mosaic of interrelated cells, the more recent dorsal part contains fewer but highly divergent cell types. This distinction could be a key to deciphering how different brain regions evolved unique roles, for example, the ventral part for basic survival and the dorsal part for adaptation, Zeng said. The atlas also uncovered how brain cells talk to each other via a diverse cast of signaling molecules, which carry messages from cell to cell. That diversity enables complex interactions between different cell types. The strong alignment across independently collected genomic, epigenomic, and spatial datasets provides high confidence that this atlas maps more than just cell identities — it captures the true organizational blueprints underlying mammalian brain development, Zeng said. Looking ahead, the atlas can serve as a model for similar mappings in the brains of other species—namely our own. That work is already underway. It also provides a guide to genetically target specific cell types, enabling tools to study specific functions and disease. This could pave the way for precision treatments, Zeng said. Allen Institute scientists also co-led a study to create a detailed map of the neurons that connect the brain to the spinal cord , enabling movement and sensory modulation. In this study, a team led by Drs. By integrating the molecular identities and locations of these neurons into one atlas, scientists gain insight into how this intricate network controls function and movement.
Jessberger, S. This algorithm is implemented in the scrattch-mapping package and publicly accessible v0. Gerstenberger, M.
Allen Brain Atlas has enormous potential to help unlock the mysteries of neurological diseases and disorders affecting millions worldwide. The Institute today announced the completion of the groundbreaking Allen Brain Atlas, a Webbased, three-dimensional map of gene expression in the mouse brain. Detailing more than 21, genes at the cellular level, the Atlas provides scientists with a level of data previously not available. About 26 percent of American adults — close to 58 million people — suffer from a diagnosable mental disorder in a given year. The project has already led to several significant new findings about the brain. It reveals that 80 percent of genes are turned on in the brain, much higher than the 60 to 70 percent scientists previously believed.
Initial installment of data and tools will be expanded and enhanced in a series of future releases. Download PDF. The Allen Institute for Brain Science announced today that it has launched the Allen Human Brain Atlas, a publicly available online atlas charting genes at work throughout the human brain. In the coming years, the Atlas will be expanded with more data and more sophisticated search, analysis and visualization tools to create a comprehensive resource useful to an increasingly wide range of scientists and research programs worldwide. The Allen Human Brain Atlas, available at www. Data modalities in this resource include magnetic resonance imaging MRI , diffusion tensor imaging DTI and histology—providing information about gross neuroanatomy, pathways of neural connections, and microscopic anatomy, respectively—as well as gene expression data derived from multiple approaches. The data in this inaugural release provide both a broad survey of gene activity throughout the entire adult human brain using microarrays, in which the entire genome can be analyzed in a single experiment, as well as more focused cellular-resolution analyses of the expression of individual genes in specific brain regions using in situ hybridization ISH , a technique that provides images of where genes are expressed at high microscopic resolution and that was used for all earlier Allen Brain Atlas resources. In addition, existing data from what was previously available as the Allen Human Cortex Study have now been integrated into the Allen Human Brain Atlas.
Allen brain atlas
A lightweight python module to interact with atlases for systems neuroscience. The brainglobe atlas API brainglobe-atlasapi provides a common interface for programmers to download and process brain atlas data from multiple sources. Full information can be found in the documentation. All the features of each atlas can be accessed via the BrainGlobeAtlas class. The various files associated with the atlas can then be accessed as attributes of the class:. There are multiple ways to work with individual brain regions. To see a dataframe of each brain region, with it's unique ID, acronym and full name, use atlas. Each brain region can also be access by the acronym, e. Working with both image coordinates and cartesian coordinates in the same space can be confusing! In brainglobe-atlasapi , the origin is always assumed to be in the upper left corner of the image sectioning along the first dimension , the "ij" convention.
Multi memu download
By establishing this baseline of the normal mouse brain, the Atlas allows researchers to compare the brain with others altered to mimic neurological and psychiatric diseases found in humans. In a set of 10 papers in Nature today, a network of researchers unveiled an atlas cataloging the location and type of every cell in the adult mouse brain. We submitted a total of genes to the Vizgen portal and selected the top genes that passed the additional filters applied by Vizgen. Inhibitory co-transmission from midbrain dopamine neurons relies on presynaptic GABA uptake. Retrieved 20 April To understand how the variety of brain functions emerge from this complex system, it is essential to gain comprehensive knowledge about the cell types and circuits that constitute the molecular and anatomical architecture of the brain. Shapovalova, J. For full subclass names, see Supplementary Table 7. Ellingwood, A. Neuropharmacology , This strategy still helped to reduce the effect of contamination from neighbouring cells due to imperfect segmentation.
The Allen Brain Cell Atlas The Allen Brain Cell ABC Atlas provides a platform for visualizing multimodal single cell data across the mammalian brain and aims to empower researchers to explore and analyze multiple whole-brain datasets simultaneously. This open science resource, developed by the Allen Institute as part of the Brain Knowledge Platform, allows unprecedented insights into the enormous diversity of cell types in the brain and where they are.
Steuernagel, L. These results support the extraordinary diversity in intercellular communications in the brain. In short, excised tissue dissectates were transferred to a well plate containing CST extraction buffer. Glia 58 , — HypoMap-a unified single-cell gene expression atlas of the murine hypothalamus. Here we report a comprehensive and high-resolution transcriptomic and spatial cell-type atlas for the whole adult mouse brain. Ren, J. Noradrenergic neurons 52 , 53 are found exclusively in subclass Cholinergic neurons 43 , 44 are found mainly in subclass 58 in the ventral PAL 11 clusters , but also include 2 clusters in LSX, 8 clusters in MH, 3 clusters in PPN, 5 clusters in dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus nerve DMX and nucleus of the solitary tract NTS , and approximately 13 clusters scattered in other medulla nuclei. Even before its announced completion, the Atlas was receiving more than 4 million hits monthly and being accessed by approximately scientists on any given work day. The result showed that all neuronal subclasses are restricted to a particular brain region, whereas non-neuronal subclasses are more widely distributed. Brain Initiative Cell Census Network. The atlas can show which genes and particular areas are effected in neurological disorders; the action of a gene in a disease can be evaluated in conjunction with general expression patterns and this data could shed light on the role of the particular gene in the disorder.

I am sorry, that has interfered... But this theme is very close to me. I can help with the answer.