Acls ecg rhythms
Use these EKG practice tests to help you become proficient in your rapid rhythm identification. Quiz complete.
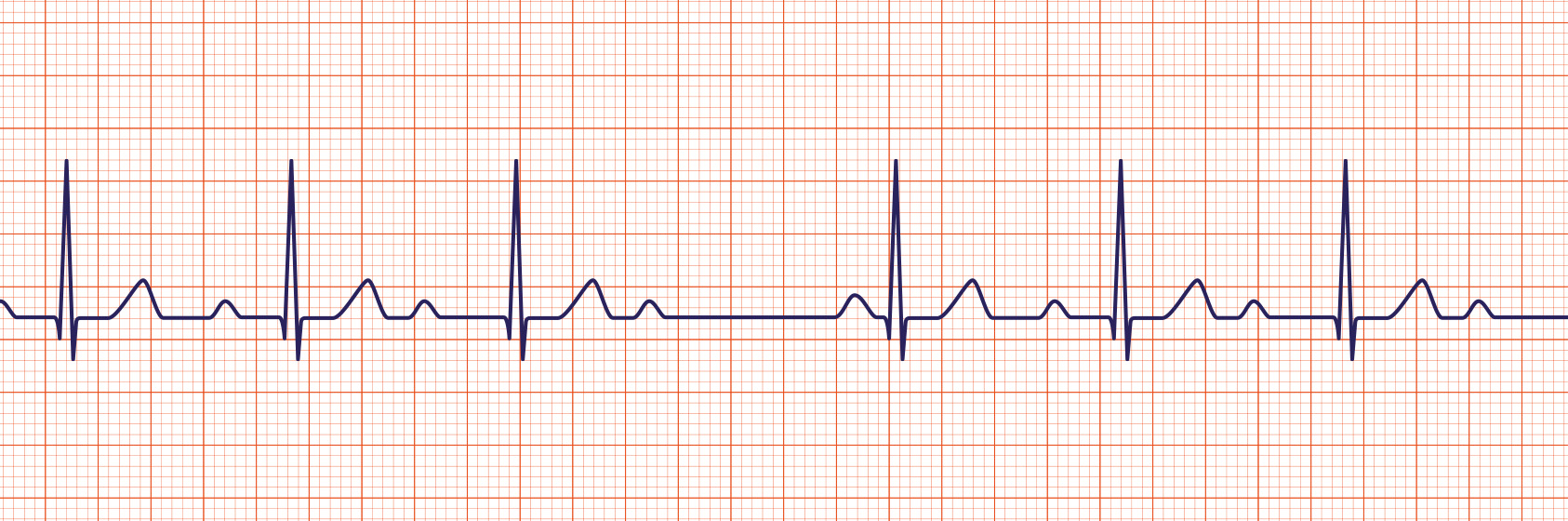
The P wave corresponds to electrical impulse traveling through the atria. This is synonymous with atrial depolarization and usually corresponds with atrial contraction. The QRS complex corresponds to the depolarization of the left and right ventricles. It generally corresponds to the contraction of the ventricles. Sinus tachycardia is a sinus rhythm with a rate greater than per minute in an adult. Note that the p waves are still present. The Mobitz Type II block must be evaluated since it is one that can rapidly progress to a complete heart block.
Acls ecg rhythms
Figure 8b. Synonymous with atrial depolarization. Reflects atrial contraction. QRS Complex Electrical activity is traveling through the ventricles. Depolarization of the left and right ventricles. Reflects ventricular contraction. T-wave Synonymous with ventricular repolarization. Reflects the start of ventricular relaxation. Reflects conduction through the atrioventricular AV node. Reflects time delay between atrial and ventricular activation. Reflects initial, slow phase of ventricular repolarization. Reflects ventricular repolarization. Reflects the period between ventricular depolarization and ventricular repolarization. Reflects a period of electrical inactivity.
QRS Complex Electrical activity is traveling through the ventricles.
These training videos are the same videos you will experience when you take the full ProACLS program. You may begin the training for free at any time to start officially tracking your progress toward your certificate of completion. Browse Videos. To successfully manage a patient who is in cardiac arrest, the caregiver must carefully, immediately, and systematically identify the cardiac rhythm and choose the most appropriate treatment algorithm. In the following lessons, we'll look at different cardiac dysrhythmias that can lead to cardiac arrest, their characteristics, and the appropriate therapies used to treat and correct the particular dysrhythmia whenever possible. However, in this lesson, we'll first look at interpreting the information on ECGs. Pro Tip 1: It's important to remember that knowing the patient's medical history, including all the events that have led up to the medical emergency, will greatly aid you in determining if there's any chance of reversing underlying causes for the cardiac arrest.
Quick Links. Frequently Asked Questions. Money-Back Guarantee. Affiliate Program. Journal Articles. About Us. Contact Us. Help Center.
Acls ecg rhythms
To understand what a dysrhythmia looks like, we must first understand each event of a normal ECG. An ECG waveform represents each electrical event in the cardiac conduction system during a cardiac cycle:. P waves are the first waveform in the complete complex, normally found upright in most leads. They represent the depolarization of both the right and left atria, which occur at the same time. The segment between the P wave and the R wave represents the delay of the electrical circuit in the AV node. This is the time it takes from the end of the P wave to the beginning of the ventricular response represented by the QRS complex. Q Waves represent the first activity of the ventricular depolarization, usually the first negative deflection after the P wave in the complete complex. The length from the end of the S wave and the beginning of the T wave is the ST segment.
Tubers93
In this section we will be discussing the different cardiac dysrhythmias that lead to cardiac arrest, their characteristics, and the appropriate therapies to treat and correct the particular dysrhythmia if at all possible. Thank you for the question. Reflects a period of electrical inactivity. It is either asystole no defined waveform or PEA. Show full transcript for ECG Interpretation video Hide Transcript So to successfully manage a patient who is in cardiac arrest, the caregiver must carefully, systematically and immediately identify the cardiac rhythm and choose the appropriate and most effective treatment algorithm. Each larger square is 5 mm in length and represents 0. To determine heart rate, count the number of QRS complexes over a 6 second interval. Ventricular Fibrillation. Onset of the QRS complex to the end of the T-wave. Multiply by The rhythm is irregular and without p waves, the rhythm is Atrial Fibrillation. When using a systematic approach for interpreting ECG rhythms, you'll help yourself and your teammates to efficiently and effectively diagnose underlying cardiac conditions. Now the R-wave is the first positive deflection after the P-wave and then is followed by the S-wave which is the first negative deflection after the R-wave. Thanks for all.
The P wave corresponds to electrical impulse traveling through the atria. This is synonymous with atrial depolarization and usually corresponds with atrial contraction. The QRS complex corresponds to the depolarization of the left and right ventricles.
Pulseless Rhythms. Keep up the good work. It should not be confused, however, with specific pulseless scenarios listed previously. Normal Sinus Rhythm. Atrial Fibrillation Afib or AF is a very common arrhythmia. Pretty much same as third degree block. And each small square is 1 mm in length and represents 0. Javascript is disabled on your browser. Reflects conduction through the atrioventricular AV node. I accept the Privacy Policy.

0 thoughts on “Acls ecg rhythms”