Carbon dioxide lewis dot
The CO 2 Lewis structure has two double bonds going from carbon to the oxygen atoms.
Carbon dioxide is a colourless, odourless, incombustible gas produced by the combustion of carbon. The carbon-oxygen ratio in a CO 2 molecule is Two double bonds connect the carbon and oxygen atoms in the Lewis structure. Two oxygen atoms are present at the terminals, where they share electrons and form bonds with the central carbon atom. Lewis structure diagrams show how many valence electrons are available within an atom for bond formation. It also allows for the visualisation of the behaviour of the valence electrons within the molecule as well as the determination of whether or not a lone pair of electrons exist. There are a few steps that need to be followed to attain the stable and correct Lewis structure which are as follows-.
Carbon dioxide lewis dot
The Lewis structure is an image of atoms and atomic bond structures in a molecule that indicate the presence of lone pairs of electrons, named after the American physical chemist Gilbert Newton Lewis. A Lewis Structure is a very simplified representation of the valence shell electrons in a molecule. Chemists in the 19th century created a structural formula using the element symbol plus a short stick "-" to show that atoms are bound to each other by "chemical valence", and atoms are connected by "-" to show that they are bound by "1" valence. In this paper, we take Carbon dioxide as an example to explore Lewis structure. Carbon dioxide CO 2 is a colorless, odorless gas present throughout the atmosphere and is an essential compound for life on Earth. The Lewis structure of CO 2 is shown below:. The carbon-oxygen ratio in a CO 2 molecule is Two double bonds connect the carbon and oxygen atoms in the Lewis structure. Two oxygen atoms are present at the terminals, where they share electrons and form bonds with the central carbon atom. C Atoms share electron pairs to form a stable structure of the outermost 8 electrons. There are two double bonds around the carbon atom. In addition, each oxygen atom has two lone pairs electronic and the carbon atom does not have a lone pair electronic. Also, there are no charges in oxygen atoms and carbon atoms.
Also, CO 2 is that chemical that humans breathe out and trees breathe in. Explain the Lewis structure of CO 2.
.
One of the postulates of the Lewis Dot Structure for representing molecules is that a bond is the result of a pair of electrons being shared between two different nuclei, and as such, can be represented as a line between the two nuclei the letters that represent the elements involved. But what if the electrons are shared between more than two nuclei? When this happens, there is no one Lewis Dot Structure that accurately describes the molecule. When this happens you need to draw resonance structures, none of which accurately describe the bonds, with the real structure sort of being the average of all the resonance structures. Sinha depicting the delocalized electrons of benzene C6H6 , which prevent one from being able to write one simple Lewis dot structure, and invoking the need for resonance structures. NOTE: Resonance structures represent different ways of placing electrons on the atoms in a molecule's Lewis dot structure. They do not describe different molecules and all resonance structures have the same connectivity.
Carbon dioxide lewis dot
Ionic bonding typically occurs when it is easy for one atom to lose one or more electrons, and for another atom to gain one or more electrons. However, some atoms will not give up or gain electrons easily. Yet they still participate in compound formation. There is another mechanism for obtaining a complete valence shell: sharing electrons. When electrons are shared between two atoms, they form a covalent bond. Let us illustrate a covalent bond by using H atoms, with the understanding that H atoms need only two electrons to fill the 1 s subshell.
Drivers optiplex 7010
Lesser known, atmospheric CO 2 also absorbs into oceans, where it can form carbonic acid, which can interfere with animals that produce calcium carbonate shells. Total electron pairs are calculated by dividing the total valence electron count by two. CO 2 hybridization is sp hybridization, with each carbon atom forming two sp hybrid orbitals. There are three resonance structures for CO 2. According to the octet rule , each oxygen atom needs to bond twice and the carbon atom needs to bond four times. Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs. CO2 Lewis Structure. FREE Signup. So it works out that C bonds with each O twice. The Lewis structure of Carbon dioxide Carbon dioxide CO 2 is a colorless, odorless gas present throughout the atmosphere and is an essential compound for life on Earth. Difference Between Atom And Molecule. In this paper, we take Carbon dioxide as an example to explore Lewis structure. So each O is surrounded by 8 total valence electrons, giving it an octet and making it stable. What is the shape of the CO 2 molecule? The presence of a sigma bond and repelling valence electron pairs forces oxygen atoms to move to the opposite side of the carbon atom, resulting in this geometric shape.
Carbon dioxide is a colourless, odourless, incombustible gas produced by the combustion of carbon.
What is it used for? The Lewis structure of Carbon dioxide Carbon dioxide CO 2 is a colorless, odorless gas present throughout the atmosphere and is an essential compound for life on Earth. Start Quiz. Each oxygen atom in the CO 2 molecule has two lone pairs of electrons. The atmospheric concentration in preindustrial times was 0. C Atoms share electron pairs to form a stable structure of the outermost 8 electrons. Also, CO 2 is that chemical that humans breathe out and trees breathe in. CO2 Lewis Properties. CO 2 hybridization is sp hybridization, with each carbon atom forming two sp hybrid orbitals. Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. The presence of a sigma bond and valence electron pairs repelling each other force them to move to the opposite side of the carbon atom, resulting in this geometric shape.

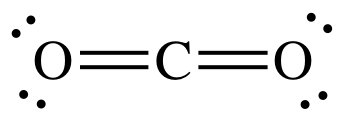
Probably, I am mistaken.
In my opinion you are not right. Let's discuss. Write to me in PM.